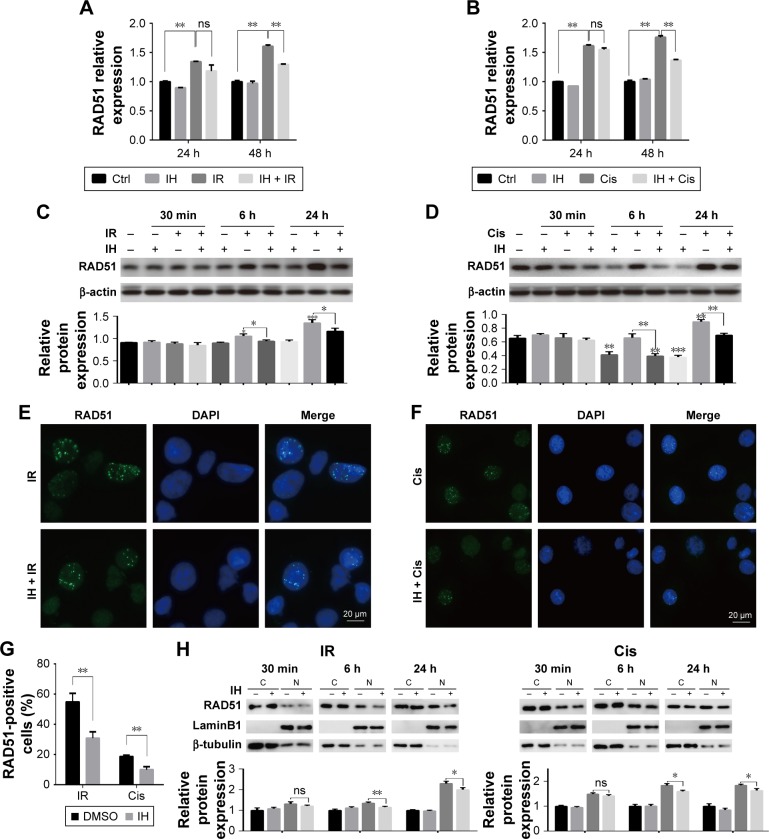
Figure 6.
Icotinib hydrochloride attenuates chemo- or radiotherapy-induced HR protein RAD51 upregulation and nuclear foci formation.
Notes: RAD51 mRNA levels at indicated time points after exposure to irradiation (A) or cisplatin (B) were detected using qRT-PCR. (C and D) RAD51 protein levels were examined by Western blotting at indicated time points post radiation (C) or cisplatin (D) treatment (top). Histograms indicate the relative protein expression levels in the cells by grayscale analysis (bottom). (E and F) Immunofluorescence stain detecting different treatment-induced RAD51 foci in Hela S3 cells. (G) Quantification of the number of RAD51 foci-positive cells after treatment.(H) RAD51 protein levels in nucleus and cytoplasm were determined separately using Western blot assays (top). Histograms indicate the relative RAD51 expression levels in the nucleus and cytoplasm by grayscale analysis (bottom). Error bars, SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test; n=3 independent cell cultures.
Abbreviations: DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; HR, homologous recombination; h, hours; min, minutes; ns, non-significant; Ctrl, control; IH, icotinib hydrochloride; IR, ionizing radiation; Cis, cisplatin; C, cytoplasmic fraction; N, nuclear fraction.