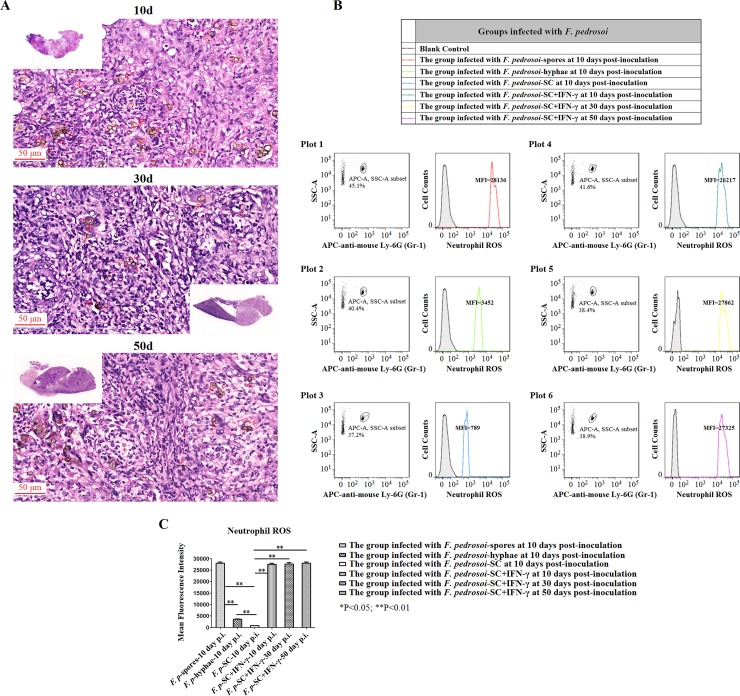
Fig 8. Exogeneous IFN-γ contributed to the formation and maintenance of micro-abscess, and restored the decrease in neutrophil ROS production in the mouse spleen infected with F. pedrosoi-sclerotic cells.
Abbreviations: F. pedrosoi-SC (F. pedrosoi-sclerotic cells); F. pedrosoi-SC+IFN-γ (F. pedrosoi-sclerotic cells and exogeneous IFN-γ) (A) HE staining (×400) for the infected spleens from the BALB/c mice intraperitoneally inoculated with F. pedrosoi-SC or with F. pedrosoi-SC+IFN-γ respectively at 10 days, 30 days and 50 days post-inoculation. The sclerotic cells with transverse septation in the infectious foci were indicated by red arrows. (B and C) Neutrophil ROS was measured in the infected spleens from the BALB/c mice intraperitoneally injected with F. pedrosoi-spores, -hyphae, -SC, and -SC+IFN-γ at the indicated days post-inoculation. (B) Flow cytometry assay was introduced to measure ROS generation in neutrophils. Briefly, the infected nodules in the spleens were aseptically isolated, and the neutrophils were selected by using side scatter (SSA) and APC-conjugated anti-mouse Ly-6G (Gr-1) mAb. The cells incubated with APC-conjugated rat-derived IgG2a kappa were set as isotype control. ROS levels in neutrophils were measured using 2’, 7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescin diacetate (DCHF-DA) as fluorescence probe, and were represented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). The neutrophils without adding DCHF-DA were set as blank control. (C) Neutrophil ROS in the infected spleens was compared among the groups of BALB/c mice mentioned above at indicated days post-inoculation. Data represent the mean±SEM (n = 4 per group at each indicated time point) and statistical analysis was performed using Univariate ANOVA and LSD-t test. Highly Significant: ** P<0.01.