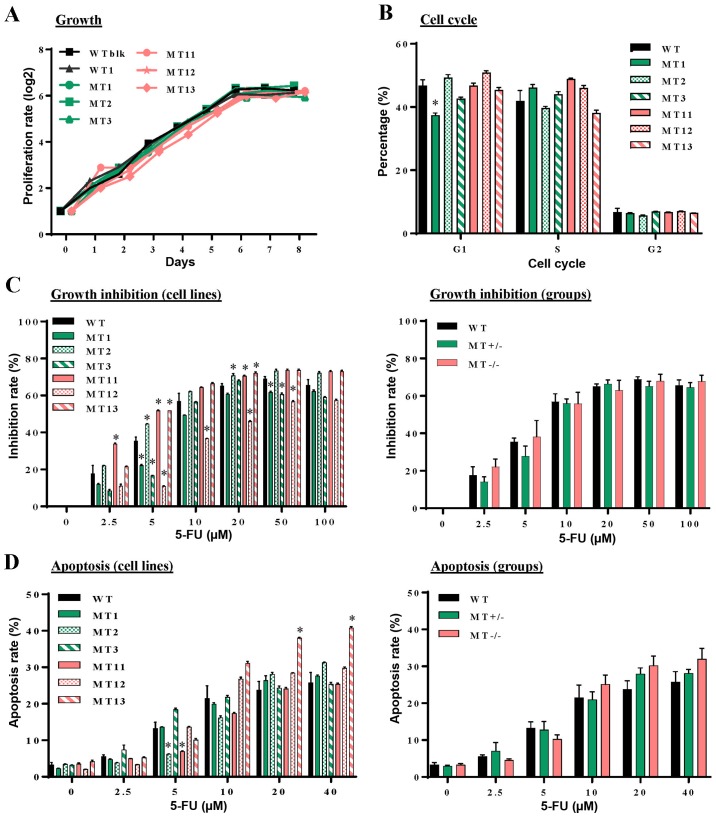
Figure 2.
Effects of CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease-mediated additional sex combs-like 1 mutations on cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and 5-FU induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. (A) Proliferation of individual WT, MT+/− and MT−/− U937 cell lines was measured at different time-points in culture by counting viable cells using a trypan blue exclusion procedure. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle progression with PI DNA staining was performed at logarithmic growth phase during the culture of WT, MT+/− and MT−/− cells. (C) Following treatment of WT, MT+/− and MT−/− cells with various concentrations of 5-FU for 48 h, cell proliferation was measured using cell counting kit-8 and inhibition rates were calculated compared with untreated samples of the corresponding cells. Left panel, inhibition rates of individual cell lines; right panel, average inhibition rates of WT, MT+/− and MT−/− U937 cell groups. (D) Following treatment with various concentrations of 5-FU, cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry with Annexin V and PI staining. Left panel, percentages of apoptotic cells in individual cell lines; right panel, average percentages of individual groups. WT in (B-D) indicates average values derived from WTblk, WT1 and WT2 cells. Data are presented as the means ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05 vs. the WT group, one-way analysis of variance. 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; CRISPR/Cas9, clustered regulaly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein-9 nuclease; PI, propidium iodide; MT, mutated; WT, wild-type; WTblk, wild-type bulk parental.