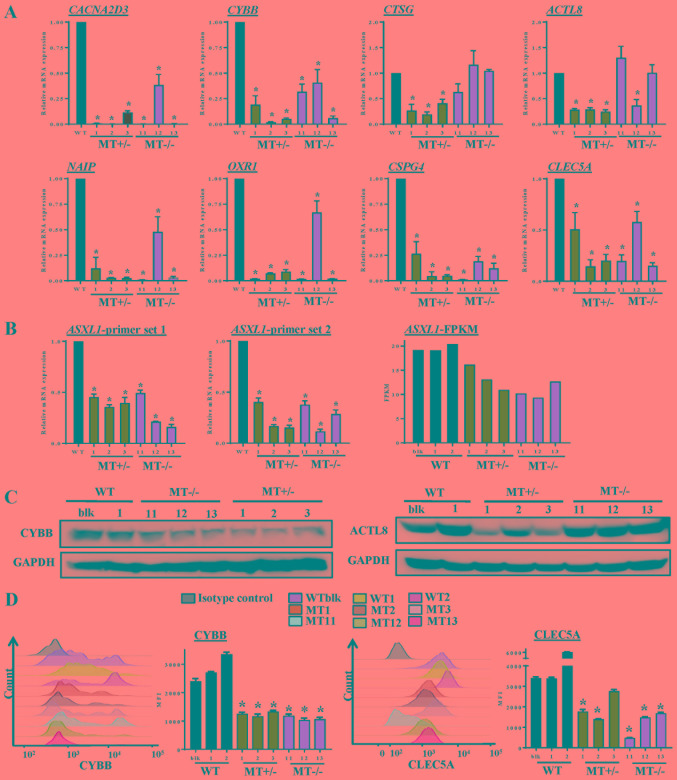
Figure 7.
Validation of RNA-seq data by RT-qPCR and immunoblotting. (A) Expression levels of genes in WT and ASXL1-mutated U937 cells were validated using RT-qPCR. Data are presented as the means ± standard error of the mean (*P<0.05 vs. the WT group, one-way analysis of variance). (B) ASXL1 expression was also validated by RT-qPCR using two primer sets targeted before (ASXL1-probe 1) and after (ASXL1-probe 2) the mutation point. FPKM values from RNA-seq data obtained from individual WT and ASXL1-mutated cell lines are also shown (ASXL1-FPKM). (C) Proteins extracted from WT, MT+/− and MT−/− cells were subjected to immunoblotting to measure CYBB and ACTL8 protein expression levels using GAPDH as a loading control. (D) Histograms of CYBB expression and MFI of CYBB (left panel), and histograms of CLEC5A expression and MFI of CLEC5A (right panel) in WT and MT U937 cells. Data are presented as the means ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05 vs. the WT group (WTblk, WT1 and WT2), one-way analysis of variance. ACTL8, actin-like 8; ASXL1, additional sex combs-like 1; CACNA2D3, calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit α2δ3; CLEC5A, C-type lectin domain family 5, member A; CTSG, cathepsin G; CYBB, cytochrome B-245 β chain; FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; NAIP, NLR family apoptosis inhibitory protein; OXR1, oxidation resistance 1; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; MT, mutated; WT, wild-type; WTblk, wild-type bulk parental.