Fig. 1.
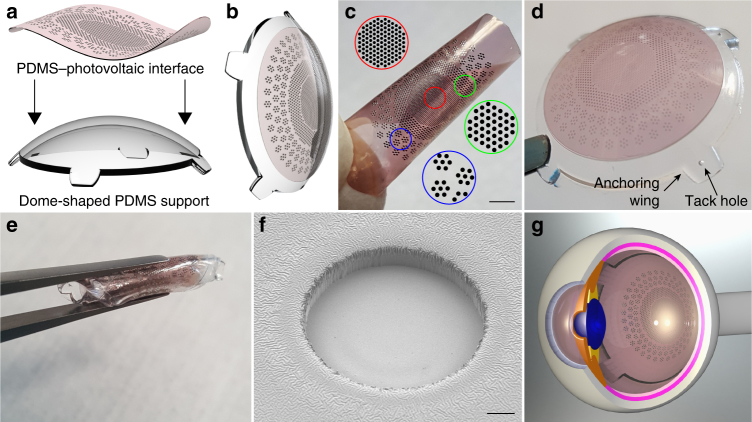
Foldable and photovoltaic wide-field retinal prosthesis. a 3D model of the fabricated PDMS-interface and of the dome-shaped PDMS support. b 3D model of the retinal prosthesis after boding the PDMS-interface to the PDMS support. c Fabricated PDMS–photovoltaic interface with pixels arranged in three areas of different sizes and densities: central area (red), diameter of 5 mm, 967 electrodes in hexagonal arrangement, electrode diameter 80 µm and pitch 150 µm, density 49.25 px mm−2; first ring (green), diameter of 8 mm, 559 electrodes in hexagonal arrangement, electrode diameter 130 µm and pitch 250 µm, density 17.43 px mm−2; second ring (blue), diameter 12.7 mm, 719 electrodes, electrode diameter 130 µm, density 9.34 px mm−2. Circles show an enlarged view of the pixels distribution. Scale bar is 2.5 mm. d Picture of POLYRETINA. Four anchoring wings with holes are present for attaching the prosthesis with retinal tacks. e POLYRETINA folded before injection. f Scanning electron microscope image (40° tilted view) of a photovoltaic pixel. Scale bar is 10 µm. g 3D model after epiretinal placement