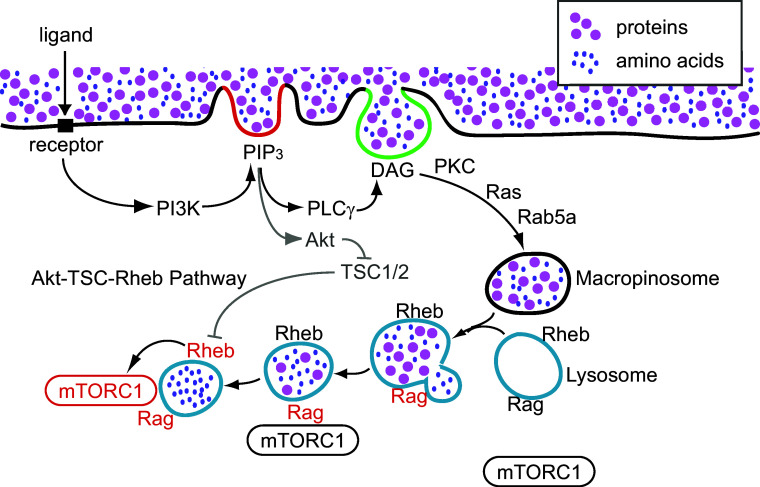
Fig. 3.
Macropinocytosis triggers mTORC1 activation. PI3K-generated PIP3 accumulates in macropinocytic cups (red line), activating Akt and PLCγ. PLCγ generates DAG in the cup (green line), leading to Ras- and PKC-dependent pathways that close the macropinosome. Extracellular nutrients internalized by the macropinosomes are delivered rapidly into lysosomes through fusion reactions. Nutrient transfer from macropinosomes to lysosomes induces Rag activation (black to red), followed by mTORC1 recruitment to lysosomes. Meanwhile, activated Akt inhibits TSC function in a cytosolic pathway independent of macropinocytosis, resulting in Rheb activation (black to red). Rheb directly activates mTORC1 on the lysosomal membranes (black to red)