Table 2.
Characteristics of published tau protein tracers updated from (Villemagne et al. 2015)
| Tracer name | Chemical structure | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pyridinyl-butadienyl-benzothiazole derivative | ||
| [11C]-PBB3 (Maruyama et al. 2013; Hashimoto et al. 2014) |
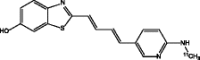
|
• Selectively binds to tau |
| • Retention of 11C-PBB3 in the venous sinuses | ||
| • Retention of tracer in basal ganglia in patient with corticobasal degeneration suggests that it might bind to non-AD tauopathies | ||
| Dialkylamino-naphthylethylidene derivative | ||
| [18F] FDDNP (Kepe et al. 2013; Thompson et al. 2009; Small et al. 2013; Shoghi-Jadid et al. 2002; Smid et al. 2013) |
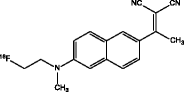
|
• First 18F-tracer with tau binding |
| • Lack of selectivity for tau; nanomolar binding affinity to Aβ | ||
| • Very limited dynamic range | ||
| • Regional brain retention used for differentiating Aβ and tau | ||
| Benzimidazole derivatives | ||
| [11C]-N-Methyl-Lansoprazole (Shao et al. 2012; Fawaz et al. 2014) |
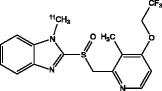
|
• In vitro binding to paired helical filament-tau demonstrated |
| • No brain uptake in mice (P-glycoprotein substrate) | ||
| • Brain uptake in non-human primates | ||
| • No human studies reported | ||
| [18F]-N-Methyl-Lansoprazole (Fawaz et al. 2014) |
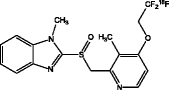
|
|
| Quinoline derivatives | ||
| [18F]-THK-523 (Harada et al. 2013) |
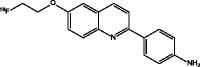
|
• Slow kinetics |
| • Non-specific binding (white matter, brain stem) | ||
| • No detection of non-AD tauopathies (Pick’s disease; three-repeat tauopathy) | ||
| [18F]-THK-5105 (Okamura et al. 2013; Okamura et al. 2014) |
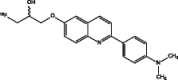
|
• Faster kinetics and higher contrast than 18F-THK-523 |
| • Non-specific binding (white matter, brain stem) | ||
| [18F]-THK-5117 (Okamura et al. 2013; Okamura et al. 2015) |
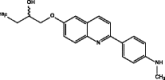
|
|
| [18F]-THK-5351 (Harada et al. 2015) |

|
• Faster kinetics and higher contrast than THK-523 |
| • Lower white matter retention | ||
| • Higher signal-to-noise ratio compared with 18F-THK-5105 and 18F-THK-5117 | ||
| 6,5,6 Tricyclic pyrimidines and indoles | ||
| [18F]-T807 (Chien et al. 2013; Xia et al. 2013) |
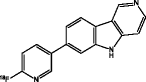
|
• Tracer with broadest clinical data package |
| • Cortical retention consistent with the known distribution of tau in AD brain | ||
| • Strong correlation with disease severity | ||
| • Slower kinetics than 18F-T808 | ||
| • Off-target activity (striatum, choroid plexus) | ||
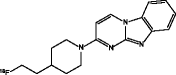
| [18F]-T808 (Chien et al. 2014) |
|
• Faster kinetics than 18F-T807 |
| • Substantial defluorination | ||
| Pyrrolo-pyridine-isoquinolineamine | ||
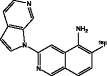
| [18F]-MK-6240 (Walji et al. 2016) |
|
• Good in vitro binding affinity to NFTs, high selectivity to β-amyloid, and excellent physicochemical properties for brain penetration and cellular permeability. |
| • No off-target binding and suitable in vivo pharmacokinetics | ||
| • Clinical studies are currently underway | ||
AD alzheimer’s disease
