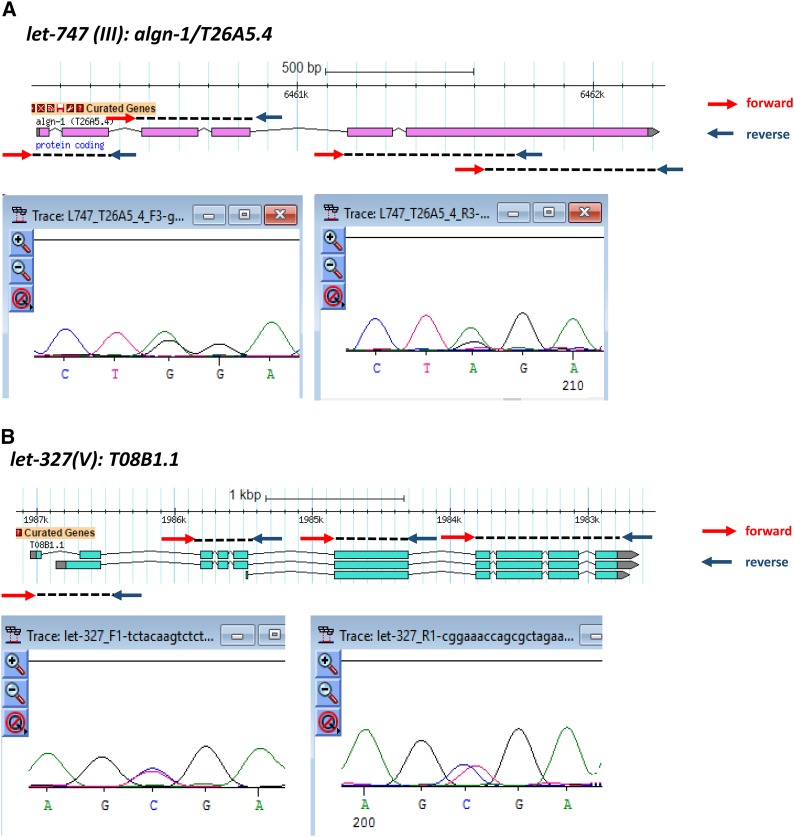
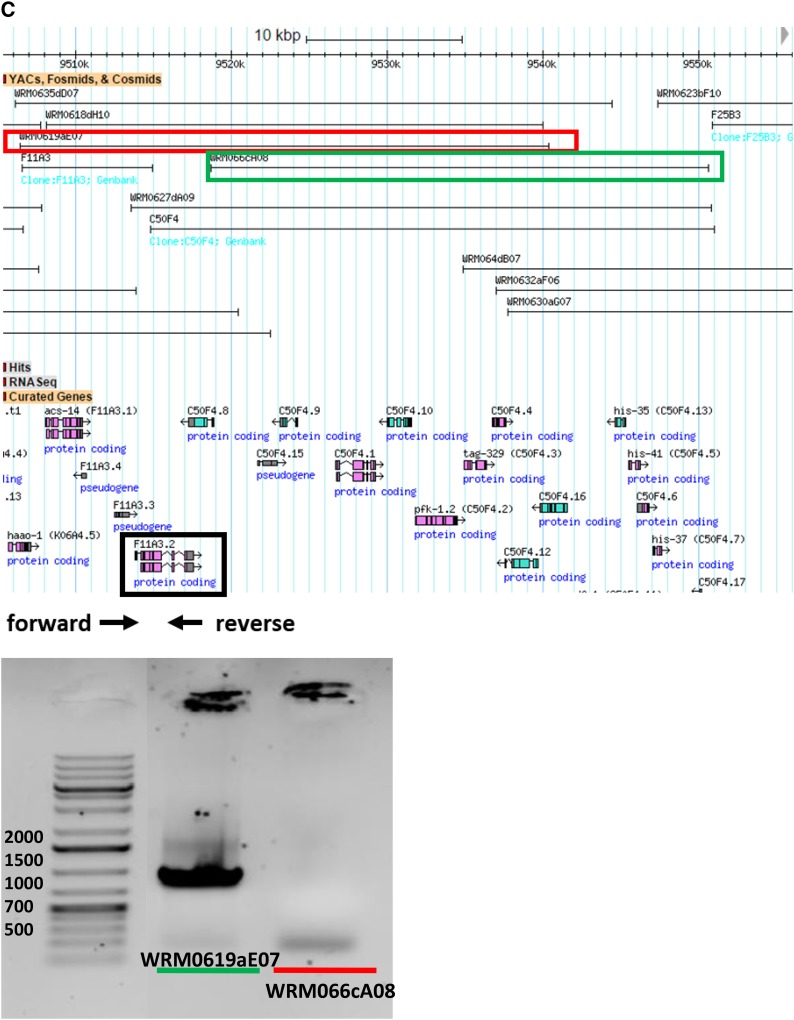
Figure 2.
Three examples of PCR sequencing validation and rescue assay. (A) Gene validation of algn-1/T26AA5.4 for let-747 on chromosome III. (B) Gene validation of T08B1.1 for let-327 on chromosome V. The gene model in each figure shows that the designed primers cover all coding exons of each gene. The red arrows are forward primers while the arrows in dark blue are reverse primers. Under each gene model, there are partials of Sanger sequencing results using forward and reverse PCR primers as sequencing primers. For let-747/algn-1/T26AA5.4, a point mutation (G->A) was found in the last exon causing a premature stop codon. A C->T point mutation was found in the second exon of T08B1.1a and the first exon of T08B1.1b. A premature stop codon occurred in both T08B1.1 transcripts because of this mutation. (C) Fosmids used for the rescue assay. The fosmid (WRM0619aE07) containing the candidate gene, F11A3.2, is in the red box while WRM066cA08 without F11A3.2 is in the green box. F11A3.2 is in the black box with the designed forward primer and reverse primer underneath. The gel image shows the presence of F11A3.2 in WRM0619aE07 with a target band of 794 bp and the absence of F11A3.2 in WRM066cA08 without the 794 bp PCR product. The weak band of ∼200 bp might be a nonspecific band because it can be found in both products using two fosmids as template.