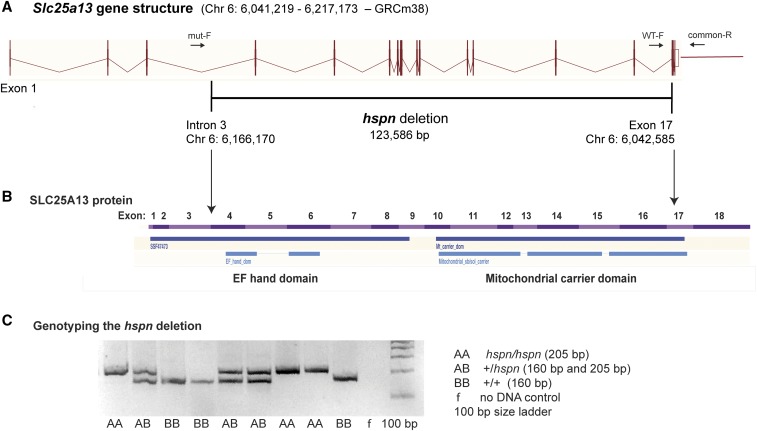
Figure 2.
Molecular characterization of the Slc25a13hspn mutation. (A) Diagramatic representation of the exon–intron genomic structure of Slc25a13. The position of the 123,586-bp hspn deletion, extending from intron 3 to exon 17, is shown as a horizontal black line. Positions of PCR primers (mut-F, WT-F, and common-R) used to genotype mice for presence or absence of the hspn deletion are shown as ↔. The wild-type allele is amplified with the WT-F forward primer and the common-R reverse primer, and the hspn deletion allele is amplified with mut-F and common-R primers. (B) Structural diagram of the SLC25A13 protein. Regions of the protein encoded by the 18 exons of the Slc25a13 gene are shown as alternating pink and purple bands. Most of the protein is deleted by the hspn mutation (indicated by the area between the ↓’s), including both the EF-hand and mitochondrial domains. The structural diagrams for the Slc25a13 gene and SLC25A13 protein were derived from the Ensembl genome browser. (C) Results from the three-primer PCR assay for the presence or absence of the hspn deletion using the mut-F, WT-F, and common-R primers shown in (A). The PCR product size for the Slc25a13 allele with the hspn deletion is 205 bp, and the PCR product size for the wild-type (+) allele is 160 bp; both product sizes are detected in +/hspn heterozygotes.