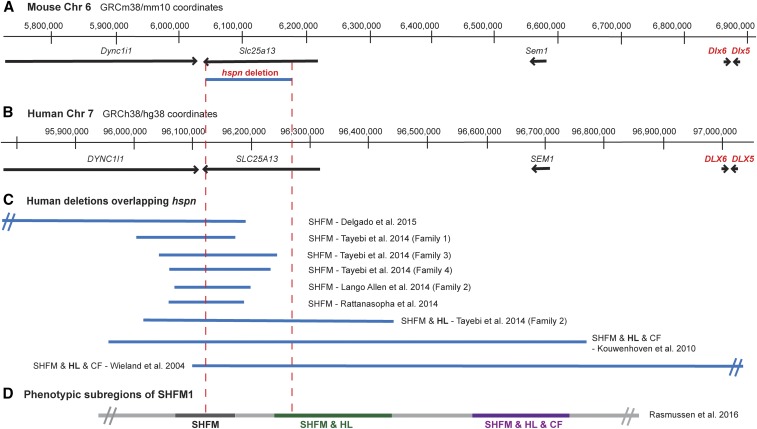
Figure 3.
Chr 6 map position of the mouse Slc25a13hspn deletion relative to Dlx5/6 and the corresponding SHFM1 region of human chromosome 7. (A) The region of mouse Chr 6 that corresponds to the human chromosome 7q21.3 region of SHFM1. Positions of the Dync1i1, Slc25a13, Shfm1, Dlx6, and Dlx5 genes are shown as horizontal black lines with arrowheads indicating the direction of transcription. The position of the Slc25a13hspn intragenic deletion is shown as a horizontal blue line. (B) The corresponding SHFM1 locus of human chromosome 7. Positions of the DYNCLI1, SLC25A13, SEM1, DLX6, and DLX5 genes are shown as horizontal black lines with arrowheads indicating the direction of transcription. (C) Deletions in SHFM1 patients that overlap with the position of the mouse Slc25a13hspn deletion (demarcated by the area between the vertical red dotted lines). The SHFM1 deletions (Wieland et al. 2004; Kouwenhoven et al. 2010; Lango Allen et al. 2014; Rattanasopha et al. 2014; Tayebi et al. 2014; Delgado and Velinov 2015) were associated with isolated SHFM, SHFM with hearing loss (SHFM & HL), or SHFM with hearing loss and craniofacial abnormalities (SHFM1 & HL & CF). The diverse SHFM1 phenotypes are thought to be the result of disrupted long-range enhancer effects on DLX5/DLX6 expression. (D) The three phenotypic subregions of the SHFM1 locus inferred from their correlations with chromosomal deletions and inversion break points (Rasmussen et al. 2016). The Slc25a13hspn deletion overlaps with part of the SHFM & HL subregion.