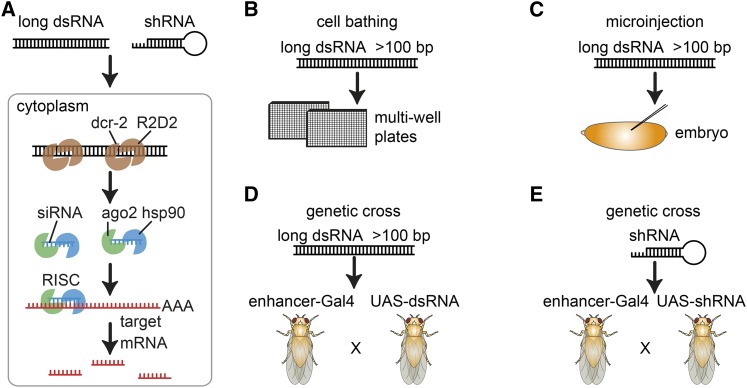
Figure 1.
RNAi methods. RNAi is a gene silencing method that works through degradation of homologous messenger RNAs (mRNA, orange). (A) In Drosophila cells, dsRNAs (black) are taken up by cells using “scavenger” receptor-mediated endocytosis. Each dsRNA/shRNA molecule is then processed by Dicer-2 and R2D2 (brown) into multiple ∼19-bp single-stranded siRNAs. These are incorporated into the RISC. RISC comprises the siRNA, AGO2 (green), and other accessory proteins (e.g., hsp90, blue) and binds and degrades the siRNA complementary target mRNA (red). RNAi can be induced (B) by bathing cells in aqueous dsRNA solution (C) by microinjections of dsRNA into embryos, (D) by crossing of transgenic (Gal4) driver lines to dsRNA-expressing flies (UAS-dsRNA), or (E) shRNA-expressing flies (UAS-shRNA).