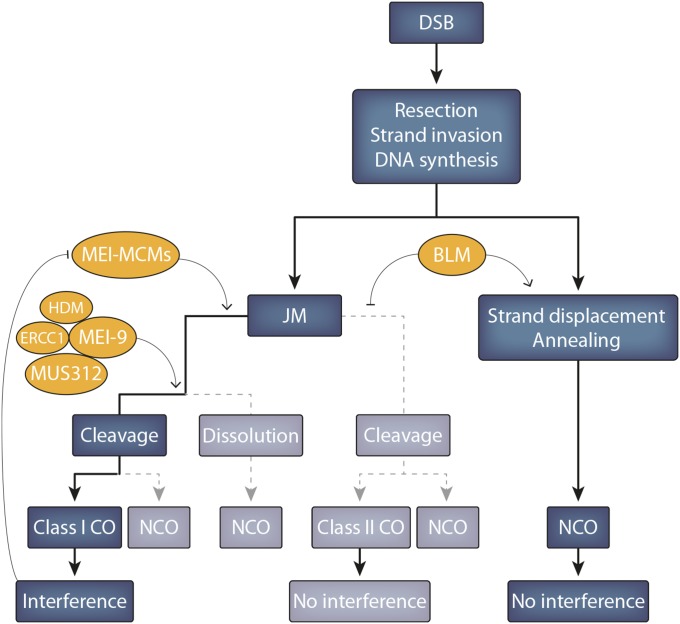
Figure 10.
Double-strand break (DSB) repair. A DSB is typically repaired as either a crossover (CO) or a noncrossover gene conversion (NCO). Two classes of COs can occur, each of which follows the formation of a joint molecule (JM). Class I COs, which are sensitive to interference, are by far the most common, while noninterfering class II COs happen infrequently under normal circumstances (rarely, a JM may be dissolved into an NCO.) The Mei-MCM proteins (Rec, Mei-217, Mei-218, and MCM5) are thought to stabilize those JMs designated to become class I COs, and the Mei-9 resolvase likely functions to cleave double Holliday junctions into COs. Under wild-type conditions, the anticrossover helicase Bloom (BLM) both inhibits class II crossovers and promotes the formation of NCOs by synthesis-dependent strand annealing.