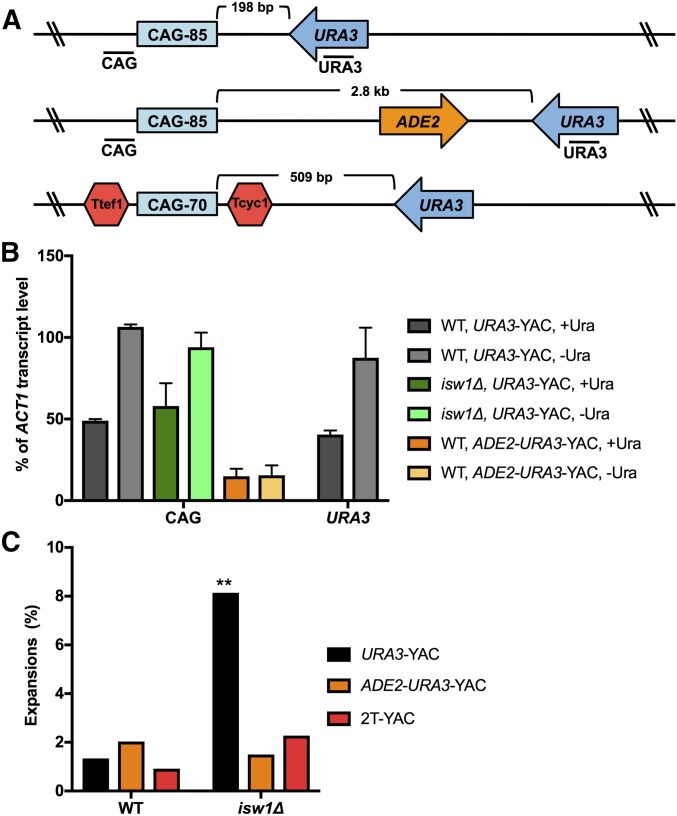
Figure 2.
Expansions occurring in the absence of ISW1 are dependent on transcription through the repeat tract. (A) Three YAC constructs were tested for repeat instability: the CAG-85 URA3-YAC (URA3-YAC) (top); the CAG-85 ADE2-URA3- YAC, where the URA3 gene has been moved far away (2.8 kb) from CAG-85 (middle); and the Ttef1-CAG-70-Tcyc1 URA3 YAC (2T-YAC), where transcription terminators (Ttef1, Tcyc1) flank the CAG repeat (bottom). Locations of PCR amplicons next to the CAG repeat and URA3 used in quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) are indicated. (B) qRT-PCR of wild-type (WT) and isw1∆ strains containing the URA3-YAC, and WT containing the ADE2-URA3-YAC in noninducing (+Ura) and inducing (−Ura) conditions. CAG transcript level is normalized to the level of ACT1 transcript and is presented as percent of ACT1 transcript level. qRT-PCR data are from two independent experiments; error bars indicate the SD. (C) The frequency of CAG repeat expansions was measured in WT and isw1∆ strains containing the CAG-85 URA3-YAC (URA3-YAC), CAG-85 ADE2-URA3-YAC, and Ttef1-CAG-70-Tcyc1 URA3-YAC (2T-YAC). Expansion frequencies were tested for significant deviation from WT using Fisher’s exact test, ** P < 0.01.