Table 2. Mammography Insurance Mandates Increased Past Year Mammography.
BRFSS 1987–2000, Adult Women 25–74
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Model is
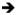
|
State and year fixed effects | (1) + linear state trends | (2) + quadratic state trends | DDD |
| Mandate specification is ↓ | ||||
| Scaled Mandate Specification | ||||
| [Annual=1; Biennial=.5; Baseline=.2] | 0.050*** (0.013) | 0.050*** (0.013) | 0.054*** (0.014) | 0.010 (0.007) |
| Adjusted R squared | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
|
| ||||
| Any Mandate Specification | ||||
| Treated by any mammography mandate | 0.037*** (0.007) | 0.037*** (0.007) | 0.040*** (0.007) | 0.005 (0.007) |
| Adjusted R squared | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
|
| ||||
| Expanded Mandate Specification | ||||
| Treated by mandate for baseline mammogram | 0.005 (0.008) | 0.003 (0.008) | 0.006 (0.007) | −0.015* (0.009) |
| Treated by mandate for biennial mammogram | 0.035*** (0.009) | 0.035*** (0.009) | 0.038*** (0.009) | 0.011 (0.012) |
| Treated by mandate for annual mammogram | 0.050*** (0.012) | 0.050*** (0.012) | 0.055*** (0.012) | 0.009 (0.007) |
| Adjusted R squared | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
Notes: Each panel of each column shows the results from a separate regression model. Sample size for all models is 693,154. The dependent variable in all models is had a mammogram in the past year. Additional controls in all models include: five-year age group dummies; Pap test mandates; state NBCCEDP implementation; laws mandating access to OB/GYNs; Medicare coverage of Pap tests and mammograms for women age 65 and older; race/ethnicity; education; marital status; share of women 15–44 with private health insurance; share of women who work or who have a husband who works at a firm with 24 or fewer employees, 25–99 employees or 100 or more employees; the unemployment rate; welfare reform; the level of HMO penetration (as a share of the population); the number of obstetric beds per 100 women 15–44; the eligibility threshold for Medicaid eligibility for a pregnant woman in the state as a share of the FPL; share urban; share black; share Hispanic; and state, year, and month of interview fixed effects. Models in column 2 add linear state trends. Models in column 3 add quadratic state trends. Models in column 4 replace the trends and state by year controls with state by age group, year by age group, and state by year fixed effects.
significant at 10%;
significant at 5%;
significant at 1%.
Standard errors throughout are clustered at the state level and estimates are weighted.
