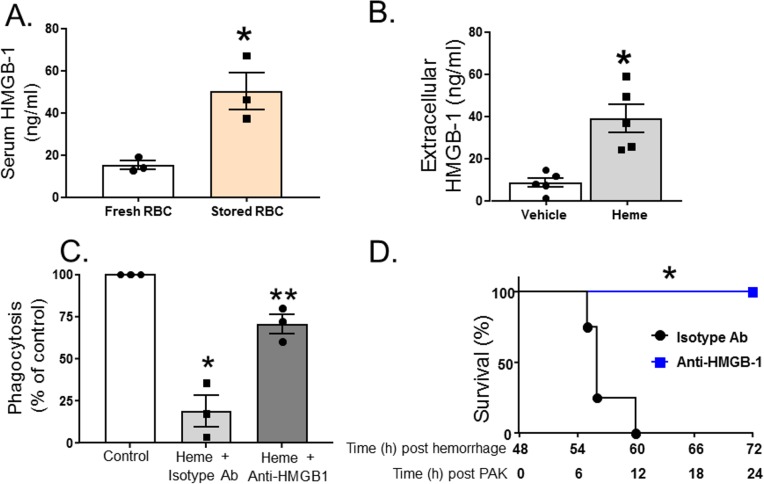
Fig 5. Heme induces exogenous release of HMGB1, which subsequently inhibits phagocytosis of P. aeruginosa by alveolar macrophages.
(A) C57BL/6 wild-type mice underwent trauma hemorrhage (TH) and were randomly resuscitated with either fresh (n = 3) or stored (n = 3) red blood cells (RBCs) with plasma (1:1). Blood was drawn 6 h after resuscitation, and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) levels were measured by ELISA. Data are mean ± SEM; each symbol represents an individual mouse. *p = 0.018 compared to mice resuscitated with fresh blood by unpaired t test. (B) Rat microvascular endothelial cell (RMVEC) monolayers were exposed to vehicle (0.01 M NaOH, n = 5) or hemin (10 μM, n = 5) for 6 h, and supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for extracellular HMGB1. Data show mean ± SEM. *p = 0.003 compared to vehicle by unpaired t test. (C) For phagocytosis assays, MH-S cells were pretreated with anti-HMGB1 blocking antibody or isotype control antibody prior to exposure to hemin and P. aeruginosa K-strain (PAK). Colonies were counted, and phagocytosis expressed as percent of control, with 100 percent being represented by colony number in plates in vehicle-treated cells. Data were collected from 3 independent experiments with 3 replicates in each experiment. Data are mean ± SEM; each symbol represents an individual experimental mean. *p = 0.023 relative to control and **p = 0.045 relative to heme + isotype antibody by 1-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey post-test. (D) C57BL/6 wild-type mice underwent TH and resuscitation with stored RBCs with plasma (1:1). Forty-eight hours later, these mice were instilled with PAK, and survival monitored. Before instillation of PAK, mice were injected peritoneally with either anti-HMGB1 blocking antibody (n = 6) or isotype control antibody (n = 4). *p = 0.001 compared to isotype control by log-rank test.