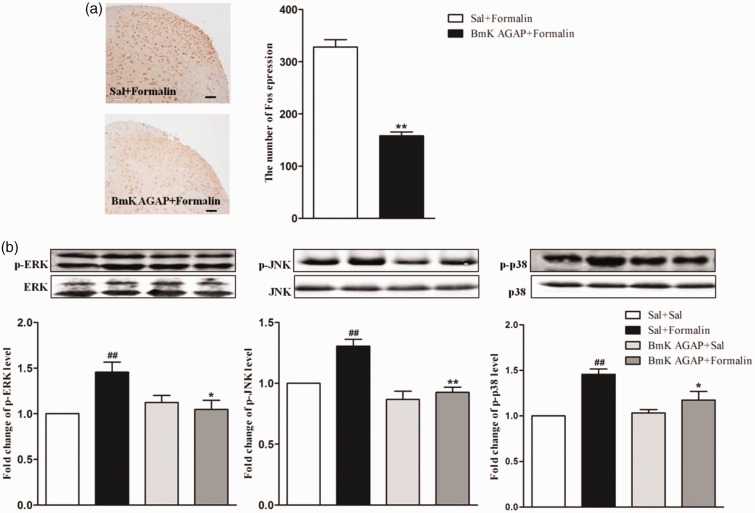
Figure 6.
Intrathecal pre-treatment with BmK AGAP inhibited formalin-induced spinal Fos protein expression, accompanied by decreased expression of spinal phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinases (p-MAPKs). (a) The representative immunohistochemical staining and quantitative data demonstrating decreased formalin-induced spinal Fos expression following pre-treatment with BmK AGAP (5 µg) in mice. **P < 0.01 compared with Sal + Formalin group; n = 6 mice in each group; scale bar = 200 µm. (b) The representative bands and the quantitative data for demonstrating modulation of spinal p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK expression following injection of formalin after pre-treatment with BmK AGAP (5 µg). The fold-change in the density of each p-MAPKs band was normalized to the total MAPK expression for each sample. The fold-change in p-MAPKs levels in the Sal + Sal group was set at 1 for quantification. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 compared with Sal + Formalin group, ##P < 0.01 compared with Sal + Sal group, n = 4 mice in each group. p-ERK: phosphorylated extracellular signal–regulated protein kinase; p-JNK: phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase.