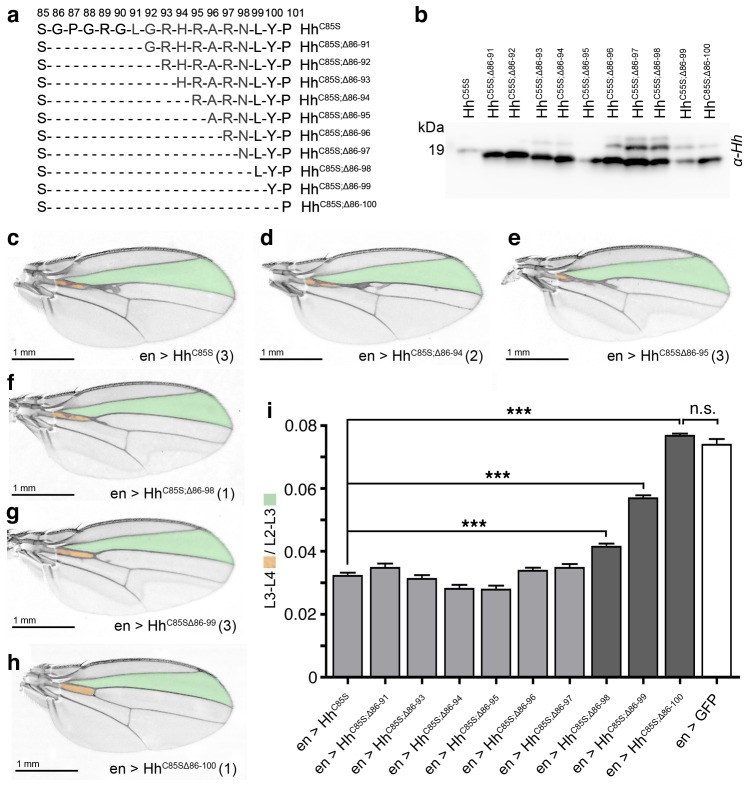
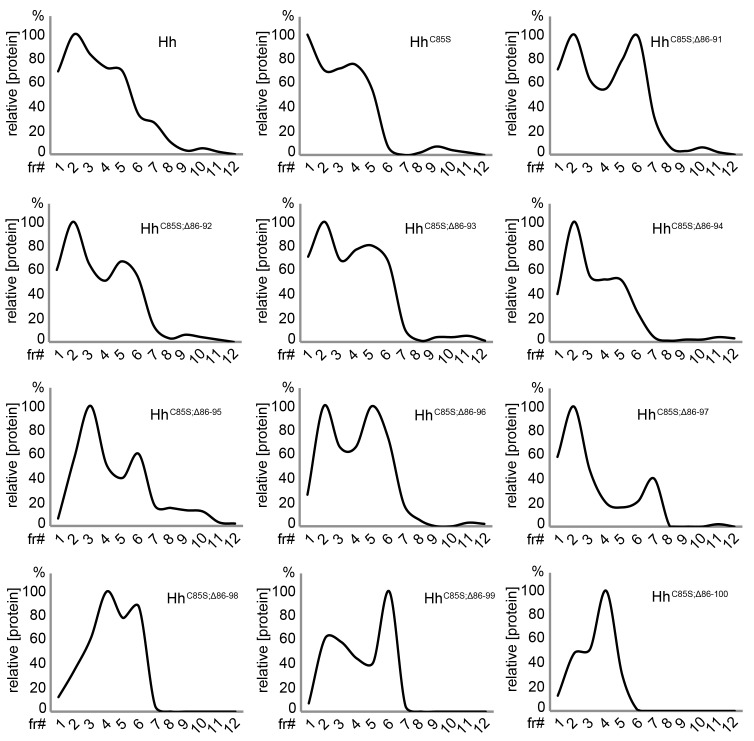
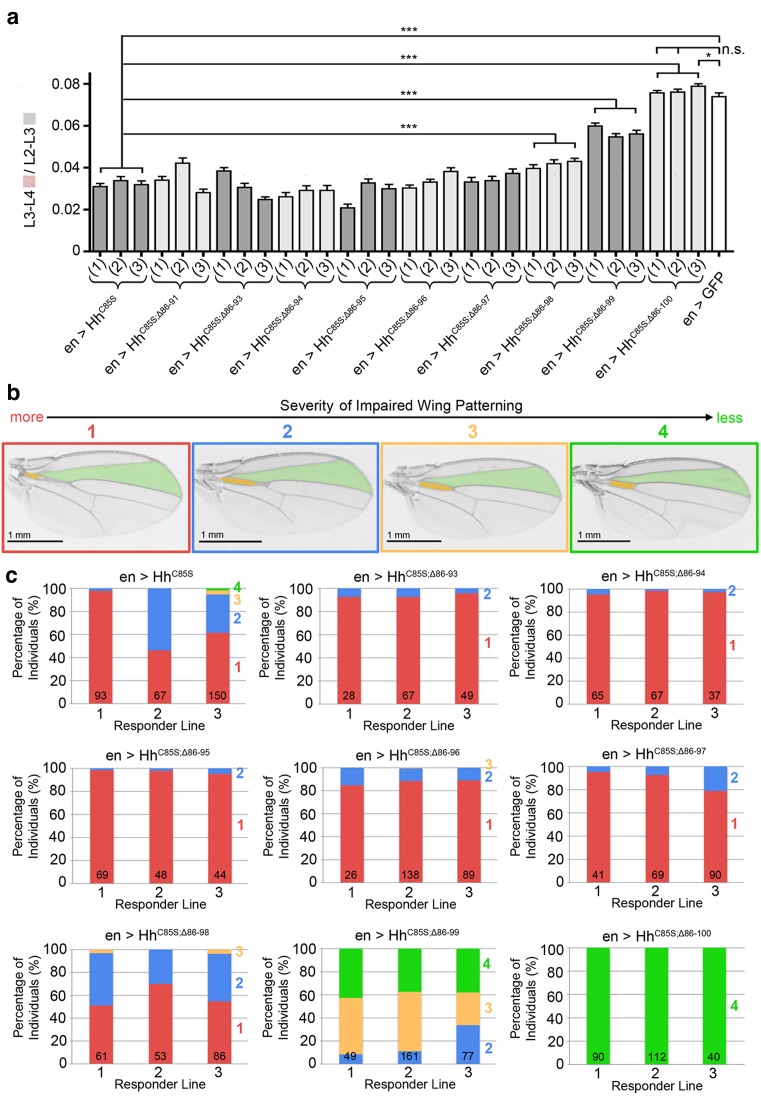
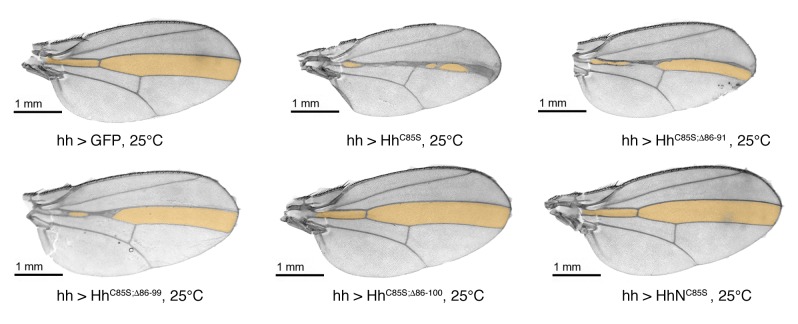
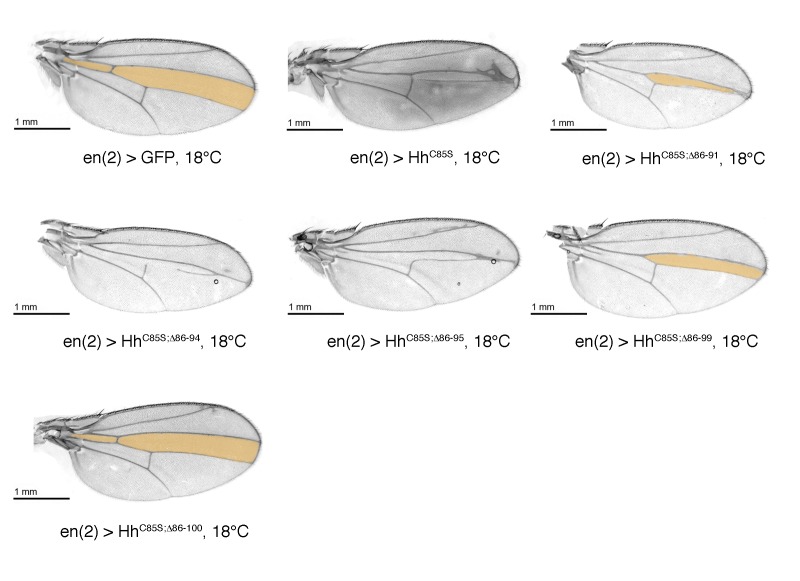
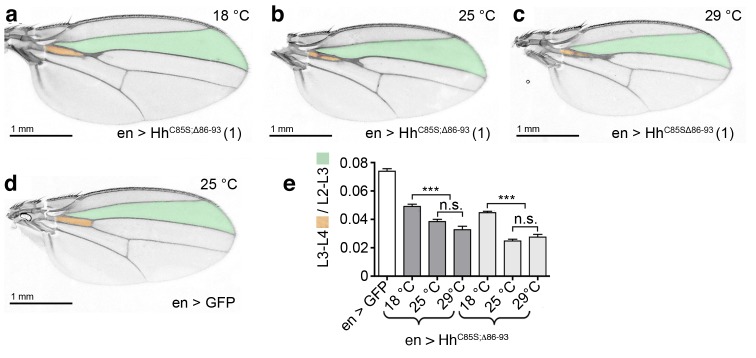
Figure 4. N-terminal truncation of palmitoylation-deficient HhC85S rescues wing formation.
(a) All truncated proteins also lacked the N-terminal cysteine, preventing Hh palmitoylation (Hardy and Resh, 2012). Residues #93–97: CW motif. (b) All proteins were expressed and secreted from S2 cells, as determined by immunoblotting. (c–h) En-regulated overexpression of HhC85S and N-terminally truncated proteins (HhC85S;Δ). Unaffected wing development despite en-regulated expression of unpalmitoylated HhC85S;Δ86-100 (h). (i) Quantification of wings shown in c-h. En-regulated GFP and HhC85S expressions served as positive and negative controls, respectively. Pooled analysis of three transgenic fly lines, each derived from an independent injection. en >HhC85S: 0.032 ± 0.001, en >HhC85S;Δ86-91: 0.035 ± 0.001 (p=0.1375), en >HhC85S;Δ86-93: 0.031 ± 0.001 (p=0.5458), en >HhC85S;Δ86-94: 0.028 ± 0.001 (p=0.0134), en >HhC85S;Δ86-95: 0.028 ± 0.001 (p=0.001), en >HhC85S;Δ86-96: 0.034 ± 0.001 (p=0.25), en >HhC85S;Δ86-97: 0.035 ± 0.001 (p=0.117), en >HhC85S;Δ86-98: 0.041 ± 0.001 (p<0.0001), en >HhC85S;Δ86-99: 0.057 ± 0.001 (p<0.0001); en >HhC85S;Δ86-100: 0.076 ± 0.0007 (p=0.0001), en >GFP: 0.074 ± 0.002. ***p≤0.001, n.s. (not significant): p>0.05, n = 60 (n = 20 per line), all flies developed at 25°C.
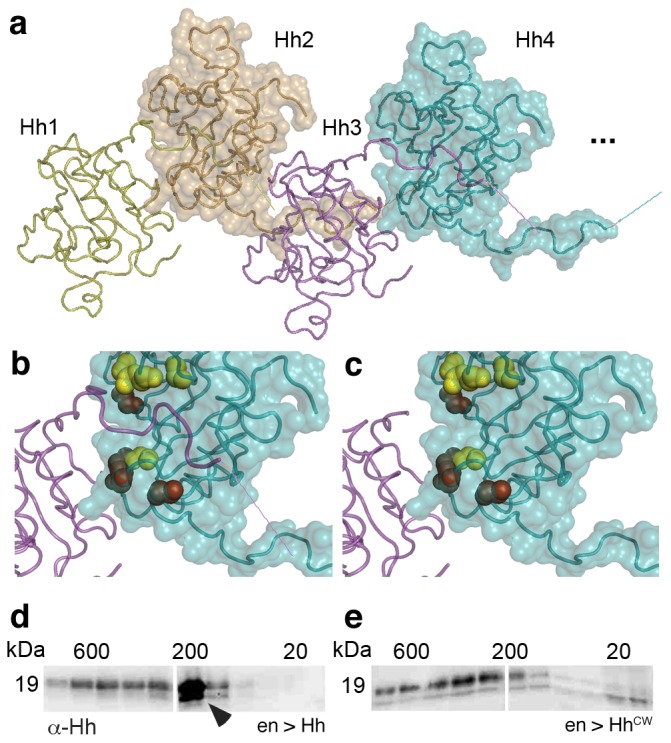
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Modeled linear Drosophila Hh clusters, using pdb 2IBG and pdb 3M1N as templates.