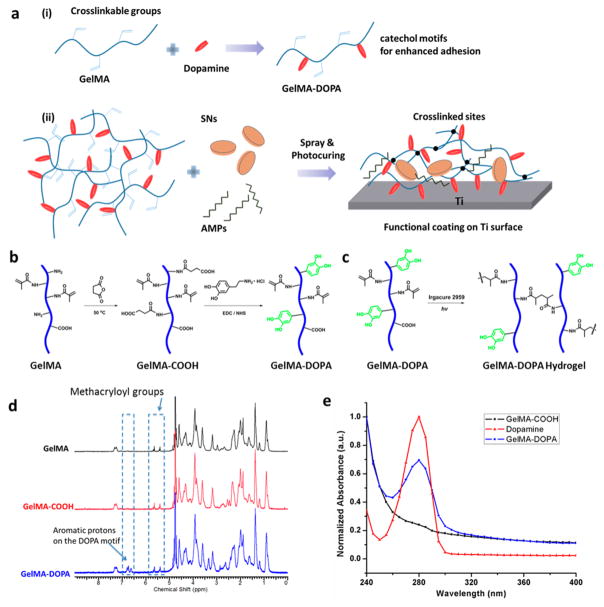
Figure 1.
Synthesis and molecular characterization of the catechol-functionalized GelMA-DOPA hydrogel. (a) Schematic illustration of the formation of a highly adhesive, multifunctional hydrogel coating on Ti surfaces: (i) GelMA was modified with dopamine to introduce the catechol motifs that bind strongly to Ti and (ii) the hydrogel prepolymer solution was then mixed with the bioactive AMP and SNs, sprayed onto implant surface, and photocured in situ to form an antimicrobial and osteoinductive hydrogel coating layer. (b) Synthetic scheme of dopamine-containing GelMA (GelMA-DOPA). (c) Formation of a cross-linked network with dangling dopamine motifs upon UV exposure in the presence of a photoinitiator. (d) 1H NMR spectra of GelMA, GelMA-COOH, and GelMA-DOPA. Comparison indicated the appearance of additional resonance peaks in the aromatic region of the GelMA-DOPA spectrum, which can be assigned to the DOPA motifs. (e) UV–vis absorption spectra of GelMA-COOH, dopamine hydrochloride, and GelMA-DOPA. Appearance of the peak centered at 280 nm indicated successful conjugation of the DOPA motifs.