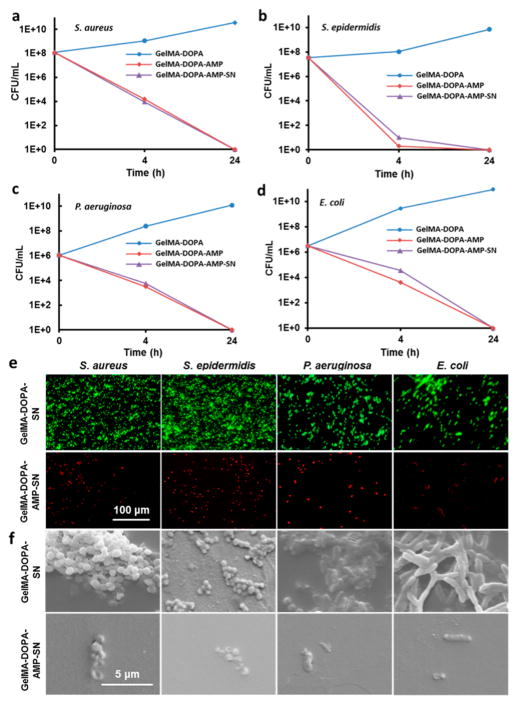
Figure 4.
Antimicrobial activity of GelMA-DOPA hydrogels at 20% (w/v) prepolymer concentration with AMP and/or SN additives. Bacteria colony count experiments against different bacteria: (a) S. aureus, (b) S. epidermidis, (c) P. aeruginosa, and (d) E. coli, seeded on different hydrogel formulations at 20% (w/v) concentration. Changes in cfu at 4 and 24 h after incubation were taken as the measure of antimicrobial ability. Error bars in parts a–d are too small to present proportionally in the panels. (e) AMP released from GelMA-DOPA–AMP–SN samples demonstrated efficient antimicrobial ability to kill the tested bacteria, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli. Compared to GelMA-DOPA–SN samples without AMP loading, no live bacteria were observed on the GelMA-DOPA–AMP–SN samples after 24 h culture (green, live bacteria; red, dead bacteria; scale bar, 100 μm). (f) SEM images showing surfaces of GelMA-DOPA–SN and GelMA-DOPA–AMP–SN hydrogels incubated overnight with S. aureus, S. epidermidis, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli. Very few bacteria were observed on the AMP-loaded samples (scale bar, 5 μm).