Fig. 4. Characterization of nanowood.
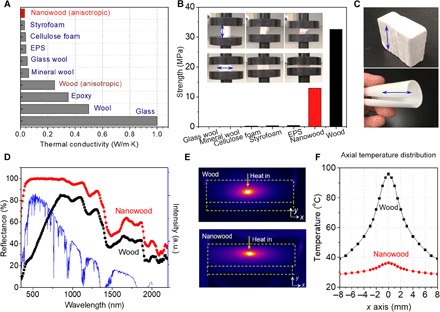
(A) Thermal conductivity comparison among existing thermally insulating materials. The nanowood exhibits a very low transverse thermal conductivity along with high anisotropy. (B) Mechanical properties of the nanowood in comparison to other materials with a thermal conductivity smaller than 0.05 W/m·K, as well as natural basswood. (C) Photographs of a bulk piece of a nanowood and a thin and rollable nanowood. The arrows indicate the alignment direction. (D) Reflectance of the nanowood. The nanowood exhibits a larger reflectance covering the spectrum of solar radiation (that is, a low solar-weighted emissivity compared with wood). The blue curve is air mass 1.5 solar spectrum. a.u., arbitrary units. (E) Infrared image of the natural wood and nanowood when illuminated by a laser with a wavelength at 820 nm. (F) Temperature profile for the samples in (E).
