Fig. 1. Crystal structure of gallenene polymorphs.
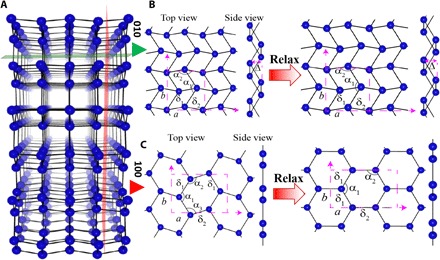
(A) Crystal structure of α-Ga. (B) Monolayer gallenene structure obtained after cleaving along the (010) direction from the bulk α-Ga as shown by the green plane. On relaxation, this forms a distorted rhombic lattice. (C) Monolayer gallenene structure obtained after cleaving along the (100) direction from the bulk α-Ga as shown by the red plane, which forms a honeycomb structure after relaxation. The unit cell of monolayer structures is represented by dashed rectangular magenta box. a and b are the cell parameters of the structure. The bond lengths and bond angles are shown by δ (in angstrom) and α, respectively. The symbol Δ (in angstrom) represents the buckling height of the monolayer gallenene structure. The cleaved a100 structure (δ1 = 2.72, δ2 = 2.54; α1 = 139.54°, α2 = 105.43°, α3 = 115.03°; Δ = 0) transformed to a graphene-like structure (δ1 = 2.51, δ2 = 2.50; α1 = 122.56°, α2 = α3 = 118.9°; Δ = 0) after relaxation using DFT. The cleaved b010 structure (δ1 = 2.77, δ2 = 2.72; α1 = 111.64°, α2 = 115.03°; Δ = 1.46) forms a quasi-2D multidecker structure (δ1 = 2.77, δ2 = 2.72; α1 = 111.64°, α2 = 115.03°; Δ = 1.32) upon relaxation. The blue balls and solid black line represents Ga atoms and Ga-Ga bonds.
