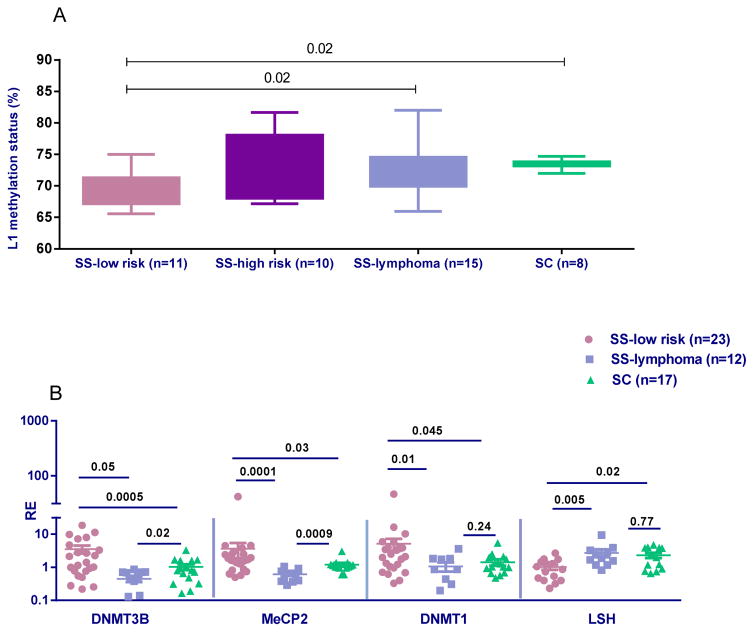
Figure 1. Methylation levels of the L1 promoter and mRNA expression of mediators of methylation in MSG tissues from SS patients and controls.
A. Statistically significant decreased mean levels of % methylation at 4 CpG sites of the L1 promoter detected by bisulphite pyrosequencing in SS-low risk patients (n=11) compared to SS-lymphoma patients (n=15) and SC (n=8) (mean±SD: 69.2±3.2 vs 72.7±4.0 vs 73.6±0.8, p-values: 0.02 for both comparisons). No other statistically significant differences were detected in L1 methylation status between 10 high risk SS patients (73.0±5.1) compared to all groups studied. Of note, a borderline significance between high- and low-risk SS was observed (p-value: 0.08). B. Relative gene expression (RE) of methylating enzymes in MSG tissues from SS-low risk patients (n=23), SS-lymphoma patients (n=12) and SC (n=17). All transcripts were measured by real-time PCR. Transcript levels of DNMT1, DNMT3B and MeCP2 were higher in SS compared to both SS-lymphoma (p-values: 0.01, 0.0005 and 0.0001, respectively) and SC group (p-values: 0.045, 0.05 and 0.03, respectively). Significantly decreased LSH levels were observed in the SS-low risk compared to both SS-lymphoma (p-value: 0.005) and SC patients (p-value: 0.02). A profound decrease of MeCP2 and DNMT3B transcripts compared to SC was observed in the SS-lymphoma group (p=0.0009 and p=0.02, respectively).