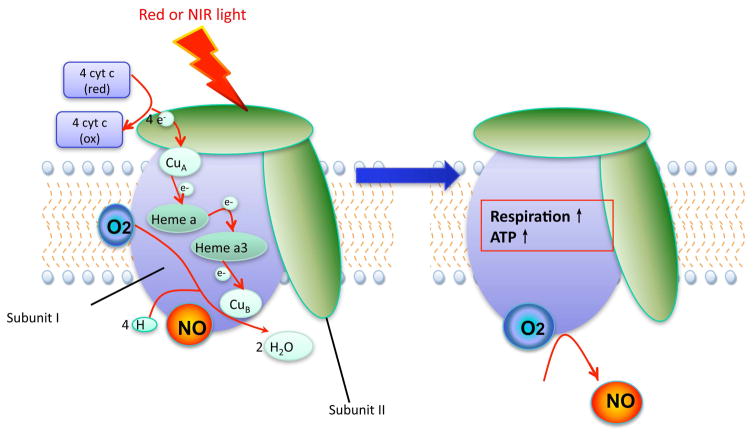
Figure 1. Proposed photodissociation of NO from cytochrome c oxidase (CCO).
CCO is a multi-subunit enzyme containing two heme co-factors and two copper centers that oxidizes four reduced cytochrome c molecules, while at the same time reducing oxygen to water and producing four protons that go on to form ATP via ATP synthase. Nitric oxide can inhibit this process by binding to CuB and it is proposed that red or NIR light can dissociate this non-covalently bound NO increasing the rate of respiration and ATP production.