Fig. 1.
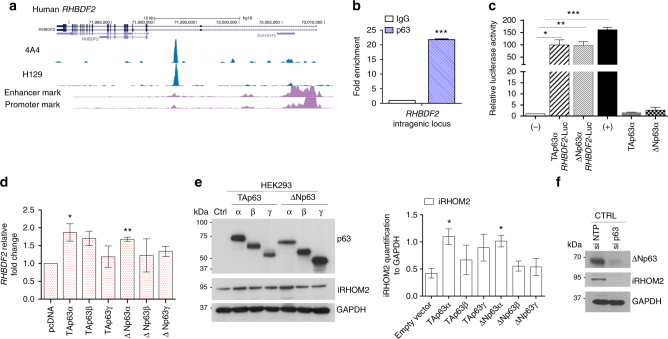
Identification of iRHOM2 as a p63 target gene in keratinocytes. a Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from ChIP-seq analysis of normal human primary keratinocytes with two different antibodies (4A4, pan-p63 and H129, α-specific). The ChIP-seq study was previously reported. b Chromatin immunoprecipitation in control keratinocytes (CTRL) with anti-pan p63 (H137) and anti-IgG antibodies followed by quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) analysis showed that p63 binds to RHBDF2 intragenic region. Error bars represent SEM of three independent experiments and Student’s two-tailed t-test value is shown; ***p < 0.001. c Luciferase assay for RHBDF2 gene locus. The construct was transiently transfected into HEK293 cells in the absence (−) or in the presence of ΔNp63α or TAp63α. The (+) control corresponds to IRF6p229-Luc plasmid. The activity of the intragenic region was measured by luciferase assay and values are expressed relative to (−) set to 1. Data were analysed using two-tailed Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001). d qRT-PCR for RHBDF2 in HEK293 cells transfected with TA and ΔNp63 isoforms. The graph represents means and SEM of three biological replicates after 9 h of transfection. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s two-tailed t-test comparing pcDNA transfected cells to other samples. e Immunoblotting of HEK293 cells over-expressing p63 isoforms, showed TA and ΔNp63 isoforms (α-pan p63) and iRHOM2 expression after 9 h of transfection. GAPDH was used as loading control. The graph represents the means of the quantification, using ImageJ software, from three independent experiments relative to GAPDH. Error bars represent SEM and Student’s two-tailed t-test values are given *p < 0.05. f Representative western blotting (WB) shows expression of ΔNp63 and iRHOM2 in normal keratinocytes (CTRL) treated with non-targeted protein (NTP) or p63 siRNAs. GAPDH was used as a loading control