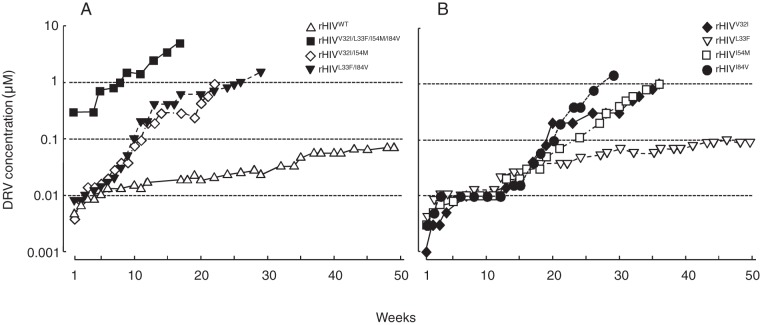
FIG 1 .
In vitro selection of highly DRV-resistant variants using various infectious HIV-1 clones. The impact of four amino acid substitutions, V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V, on the development of DRV resistance was examined. (A and B) rHIVWT, rHIVV32I/I54M, rHIVL33F/I84V, and rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V (A) and rHIVV32I, rHIVL33F, rHIVI54M, and rHIVI84V (B) were propagated in the presence of increasing concentrations of DRV in MT-4 cells. At the conclusion of each passage, cell-free supernatant was harvested from the culture and subsequently added to a following culture replenished with the same number of uninfected target cells, and the virus was further propagated. This passage was repeated every 1 to 3 weeks for a total of 17 to 50 weeks.