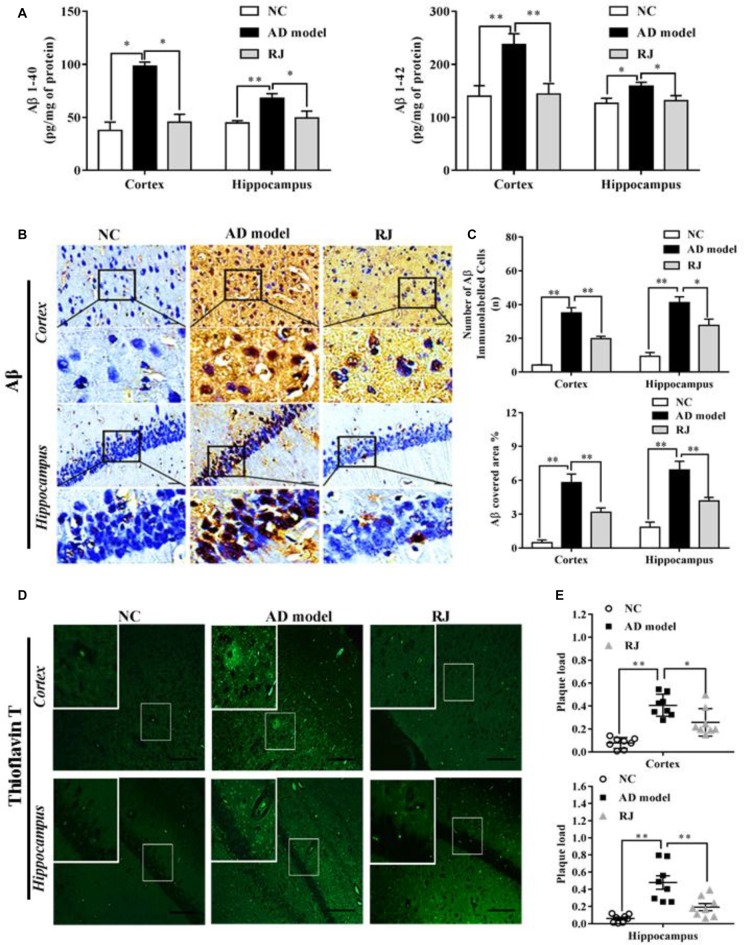
Figure 2.
Royal jelly (RJ) decreased brain amyloid β (Aβ) levels and alleviated Aβ pathology in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) rabbits. (A) The levels of Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 in the cortex and the hippocampus of each group measured by ELISA, n = 6 rabbits per group. (B) Representative Aβ-staining images in the cortex and the hippocampus of each group. Scale bar = 50 μm. Black squares indicate images with higher-magnification. Aβ positive (brown-colored) was detected mainly in the cytoplasm of neuronal cells and the cytoplasm and membranes of endothelia cells. (C) The number of Aβ immunolabeled cells per view (40×) and the covered area of Aβ staining in the brain of each group, n = 6–8 rabbits per group. (D) An example image of Aβ plaque immunoreactivity in the cortex and the hippocampus of each group by thioflavin-T staining. Scale bar = 50 μm. White squares indicate images with higher-magnification. (E) Quantification of thioflavin-T positive deposits in the cortex and the hippocampus of the three groups, n = 8 rabbits per group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test was used (A,C,E). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the AD model group.