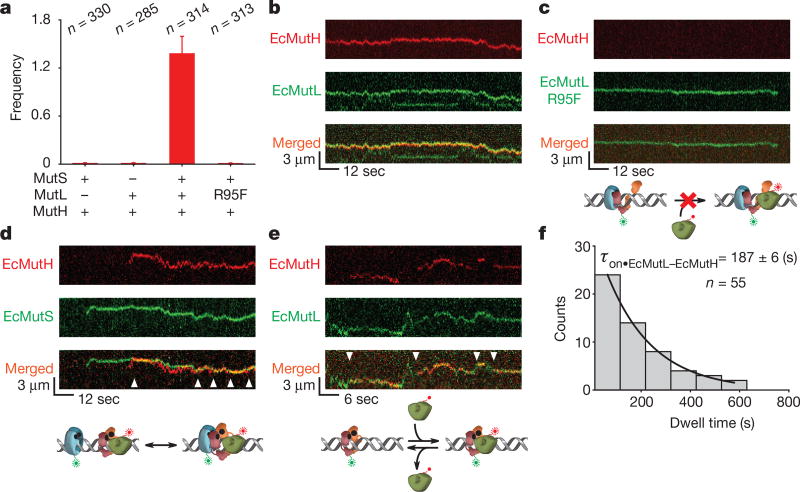
Figure 4. EcMutH binds EcMutL sliding clamps.
a, The frequency of EcMutH–AF647 on the mismatched DNA in the presence of other MMR components (mean ± s.d.). b, Representative kymographs of EcMutH–AF647 co-localization and diffusion with EcMutL–Cy3 (and unlabelled EcMutS) on a single mismatched DNA. c, Representative kymographs of EcMutL(R95F)–Cy3 (and unlabelled EcMutS) diffusion on a single mismatched DNA. Note the absence of EcMutH–AF647. d, Representative kymographs of EcMutH–AF647 co-localization and diffusion with EcMutS–AF555 (and unlabelled EcMutL) on a single mismatched DNA. Arrowheads indicate association of EcMutS with EcMutL–EcMutH. e, Representative kymographs of EcMutH–AF647 co-localization and diffusion with EcMutL–Cy3 on a single mismatched DNA following the dissociation of EcMutS. Arrowheads indicate association of EcMutH with EcMutL sliding clamp. f, Dwell time distribution of the EcMutL–EcMutH complex (τon•EcMutL–EcMutH; mean ± s.e.m.).