Fig. 3.
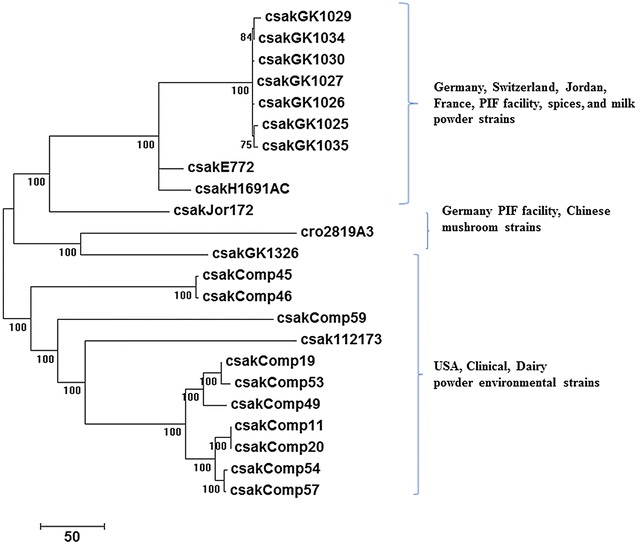
kSNP3 whole genome SNP analysis. Using the kSNP3 [33] SNP-finding tool, 1.6 million positions with SNP information across 23 malonate-positive C. sakazakii genomes were identified. The average size of C. sakazakii genome used in this analysis was approximately 4.54 MB and approximately 220,000 SNP positions across these genomes were used in the analysis. The phylogenetic tree was generated using the SNP-matrix algorithm provided by the kSNP3 tool. The numbers in the nodes denote bootstrap values. Mega 7.0 without gaps was used to align the sequences and develop the phylogenetic tree. The ST64 C. sakazakii strains grouped into two major clusters: the first comprised strains from the German PIF manufacturing facility; and the second cluster was comprised of strains which came from the USA diary powder manufacturing facilities. Several C. sakazakii ST64 strains such as E772, H1691AC, and Jor172 which came from a milk powder sample from France; a Swiss PIF manufacturing facility sample; and a Jordanian spice sample share greater phylogeny with that of the German PIF strains, respectively. Additionally, three USA diary powder manufacturing facility strains and the clinical strain from the USA were also more related to the European and Middle East strains than the second cluster of USA diary powder manufacturing facilities strains. Bar marker represents 0.00020 nucleotide differences per 10,000 positions
