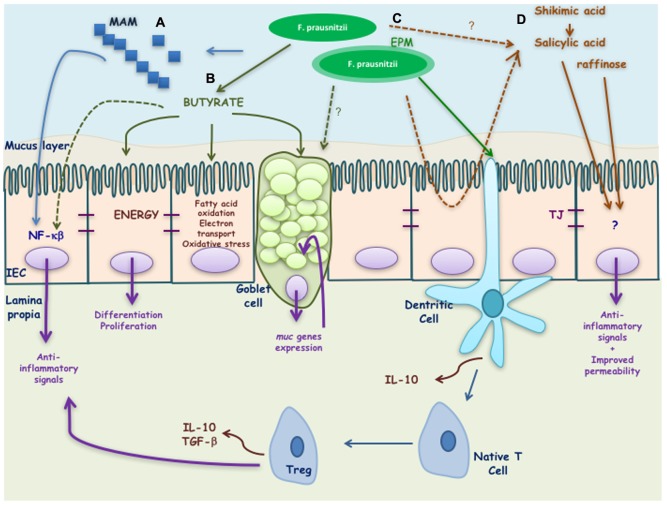
FIGURE 2.
Putative effectors of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and its effects on the host. F. prausnitzii exerts its benefic effects by means of different effectors: (A) MAM peptides secreted by F. prausnitzii block NF-κB activation induced by a pro-inflammatory stimulus. (B) Butyrate produced by F. prausnitzii inhibits NF-κB activation and interacts with the intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) driving to the activation of different genes involved on the differentiation, proliferation, and restitution of enterocytes. It is also involved on the regulation of fatty acid oxidation, electrons transport chain, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. In goblet cells it has been described to stimulate muc genes allowing a high production of mucus. (C) EPM produced by F. prausnitzii modulates IL-10 cytokine production in antigen presenting cells. Finally, (D) salicylic and shikimic acids are anti-inflammatory molecules able to block inflammation induced by a pro-inflammatory stimulus while raffinose is key in maintaining gut permeability.