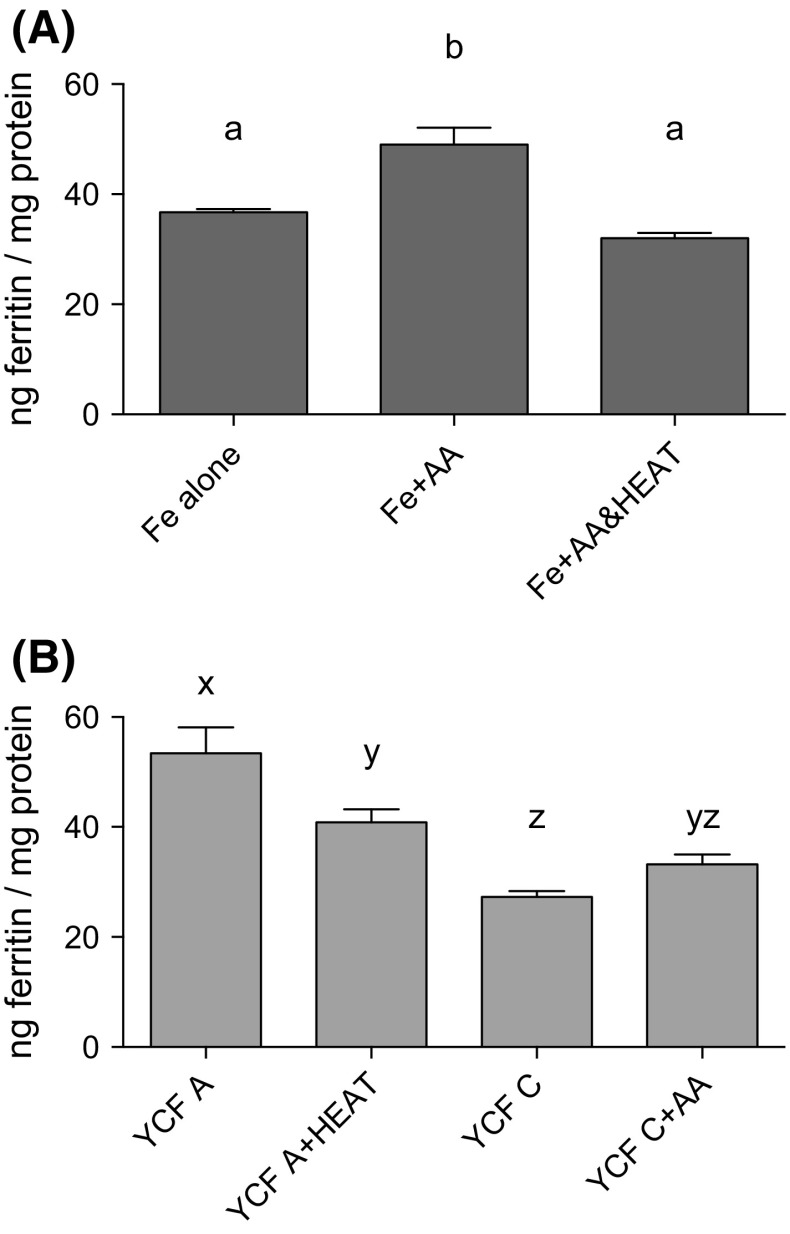
Fig. 2.
a Ferritin levels of Caco-2 cells exposed to control digests, both with, and without, heat treatment to degrade ascorbic acid (AA). Heat treatment of the positive control (Fe + AA at a 1:10 Fe/AA molar ratio) decreased the enhancing effect of AA on iron uptake; ferritin formation was equivalent between the Fe alone and Fe + AA controls. Based on an ANOVA (p = 0.0003) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, post hoc analysis done on an all-pairwise basis; means with different superscript letters in a column are statistically different (p ≤ 0.0015). b Caco-2 ferritin levels of cells treated with YCF A digestates, with, and without, heat treatment, and YCF C digestates, with, and without, added AA (≈1:4 Fe/AA molar ratio). Ferritin levels of YCF A decreased after heat treatment; ferritin levels of YCF C increased after the addition of AA to levels equivalent with YCF A; however, ferritin was still less than non-heat-treated YCF A levels. All presented values are means normalised to the Fe reference control (Fe alone) ± SEM. Based on an ANOVA (p < 0.0001) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, post hoc analysis done on an all-pairwise basis; means with different superscript letters in a column are statistically different (p ≤ 0.0074)