Fig. 7.
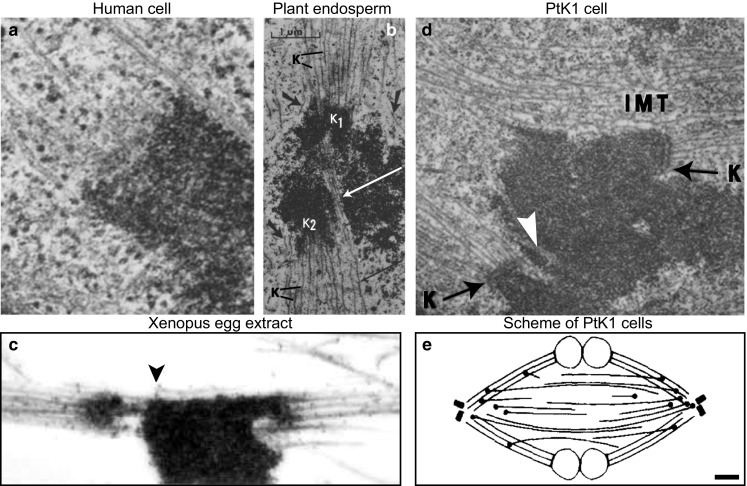
Interpolar microtubules are found in the vicinity of kinetochore microtubules and kinetochores during metaphase. Example images of metaphase spindles from different organisms, obtained by using electron microscopy, are shown. a Area around a kinetochore in a human WI-38 cell. Several microtubules end at the kinetochore, whereas a non-kinetochore microtubule passes the kinetochore zone. Image reproduced with permission from (McIntosh and Landis 1971). b Area around kinetochores in the spindle of Haemanthus katherinae endosperm. Two kinetochores (K1 and K2) are attached to kinetochore microtubules (K). Non-kinetochore microtubules (long arrows) intermingle with kinetochore microtubules. Image reproduced with permission from (Jensen 1982). c Area around kinetochores in a Xenopus egg extract spindle. Kinetochore fibers are associated with microtubules that do not end at kinetochores (arrowhead). Image reproduced with permission from (Ohi et al. 2003). d Area around kinetochores in a PtK1 cell. Interpolar microtubules (IMT) and microtubules which penetrate the chromosome (white arrow) are found near the kinetochores (K). Magnification ×21,000; image reproduced with permission from (Brinkley and Cartwright 1971). e Arrangement of interpolar and kinetochore microtubules in a metaphase PtK1 spindle, based on reconstructions of microtubules from electron micrographs. Black circles mark the minus ends of interpolar microtubules, which are found farther from the pole than those of kinetochore microtubules and most are in or near kinetochore fibers. Scale bar 1 µm; image reproduced with permission from (Mastronarde et al. 1993)
