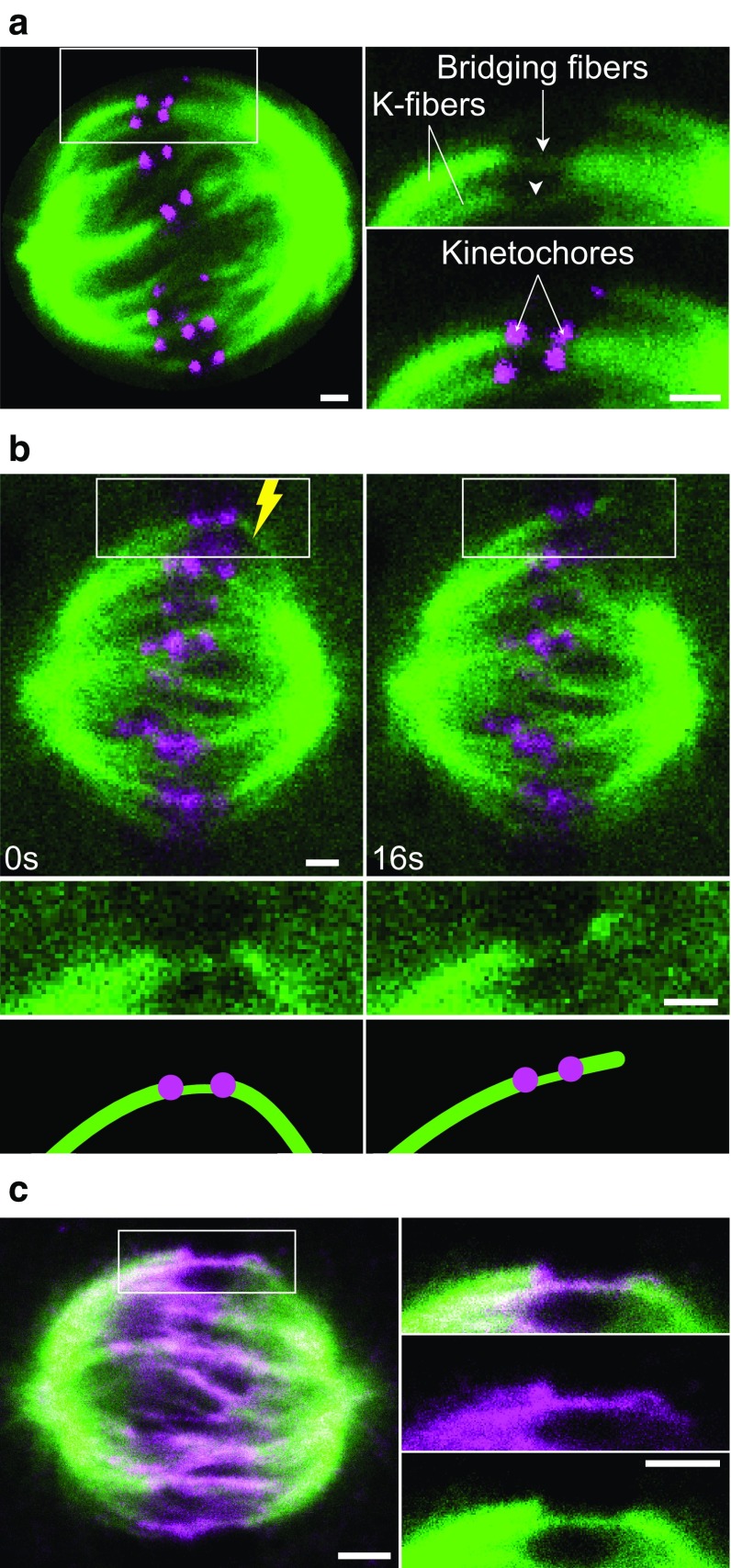
Fig. 8.
Bridging microtubules link sister kinetochore fibers. a Spindle in a HeLa cell with microtubules shown in green (stained with SiR-tubulin) and kinetochores in magenta (EGFP-CENP-A). Enlargements of the boxed region (top tubulin, bottom merge) show bridging fibers connecting sister kinetochore fibers (k-fibers). Compared with kinetochore fibers, bridging fibers contain fewer microtubules and hence are less bright. b Laser ablation of a kinetochore fiber in a HeLa cell with microtubules shown in green (tubulin-GFP) and kinetochores in magenta (mRFP-CENP-B). Time-lapse images of the spindle (top) and enlargements of the boxed region (middle tubulin, bottom schemes) are shown. After the cut (yellow lightning sign), the bridging fiber moved together with sister kinetochores and their fibers in the direction away from the spindle. Image reproduced with permission from (Kajtez et al. 2016). c Spindle in a HeLa cell with microtubules shown in green (tubulin-GFP) and endogenous PRC1 in magenta (immunostained, Alexa Fluor-555 labeled). Enlargements of the boxed region (top merge, middle: PRC1, bottom tubulin). The PRC1 signal is found in the central part of the bridging fiber, extending ~2 µm poleward from each kinetochore. Image reproduced with permission from (Polak et al. 2017). Scale bars in all panels are 1 µm