Table 1.
Interpretation of the 16 R-regulations between vertices u and v for an R-graph.
| Depiction | Meaning | Acronym | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Mandatory, positive, unambiguous | MPU | R+∧¬R− |
 |
Mandatory, negative, unambiguous | MNU | ¬R+∧R− |
 |
Mandatory, ambiguous | MA | R+∧R− |
| No regulation | NR | ¬R+∧¬R− | |
 |
Mandatory, positive, possibly ambiguous | MPPA | R+ |
 |
Mandatory, negative, possibly ambiguous | MNPA | R− |
 |
Mandatory, unknown sign, unambiguous | MUSU | ¬(R+ ↔ R−) |
 |
Mandatory, unknown sign, possibly ambiguous | MUSPA | R+∨R− |
 |
Optional, positive, unambiguous | OPU | ¬R− |
 |
Optional, negative, unambiguous | ONU | ¬R+ |
 |
Optional, ambiguous | OA | (R+↔R−) |
 |
Optional, positive, possibly ambiguous | OPPA | R+∨¬R− |
 |
Optional, negative, possibly ambiguous | ONPA | ¬R+∨R− |
 |
Optional, unknown sign, unambiguous | OUSU | ¬(R+∧R−) |
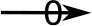 |
Contradiction | False | 0 |
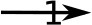 |
Tautology | True | 1 |
Each R-regulation is denoted by an acronym. Leaving out trivial regulations false, NR, and true, R-regulations can be classified as optional or mandatory. In the case of no regulation (NR), edges are not depicted. The last column shows the constraint added by Griffin in each case (R+ denotes a positive regulation from u to v for the Boolean network f (R+(u, f, v)), R− a negative regulation (R−(u, f, v)), see definition 3).
