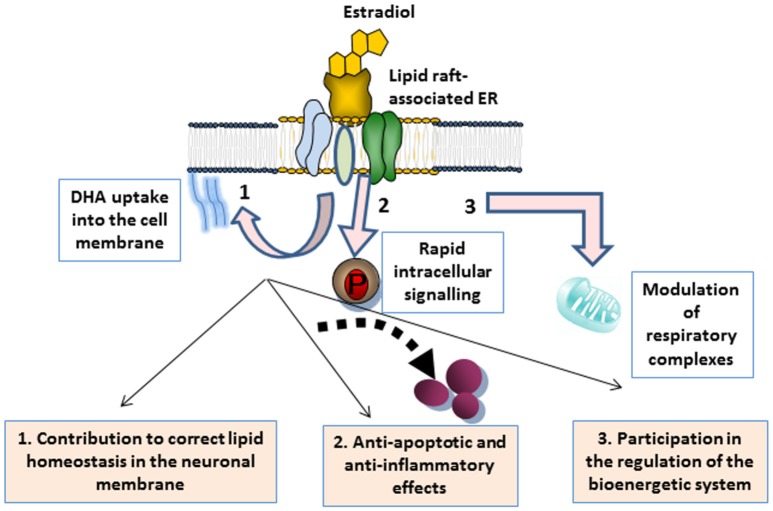
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of multiple actions of estrogen associated with neuronal membrane microdomains. 1 Estrogen binding to ERs integrated in lipid raft signalosomes triggers the rapid activation of rapid signal transduction, ultimately leading to the modulation of either anti-apoptotic or anti-inflammatory factors that contribute to neuronal maintenance. 2 The hormone also contributes to membrane lipid homeostasis, such as DHA membrane uptake, thus promoting healthy protein clustering and activities. 3 Estrogen is also an energetic and metabolic capacitor, through the participation in the mitochondrial membrane turnover and the regulation of mitochondrial supercomplexes that regulate the cell bionergetic system.