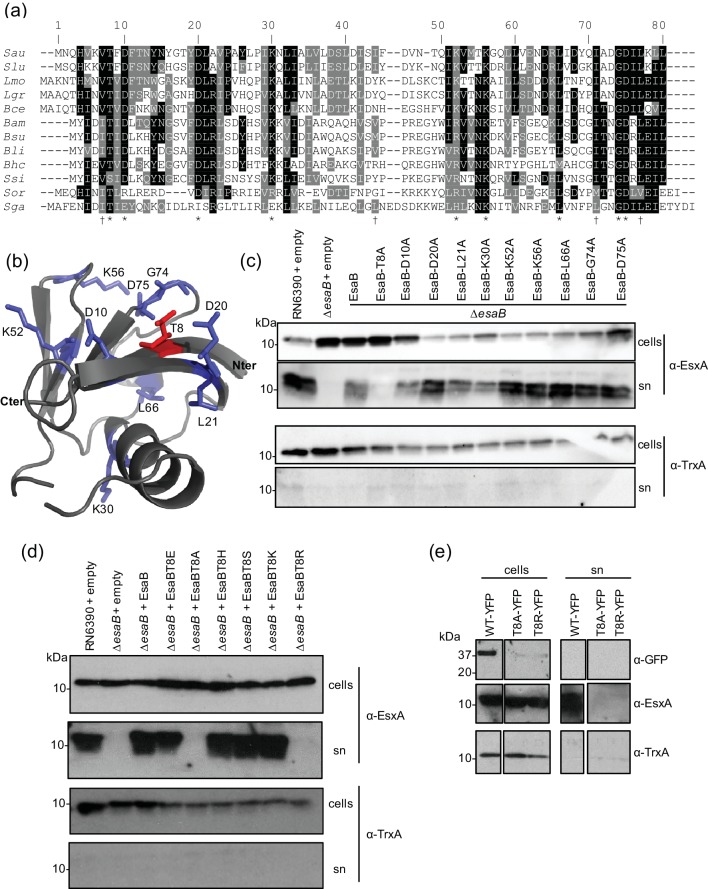
Fig. 5.
Site-directed mutagenesis of conserved residues of EsaB. (a) Sequence alignment of EsaB homologues from: Sau-Staphylococcus aureus; Slu-Staphylococcus lugdunensis; Lmo - Listeria monocytogenes; Lgr-Listeria grayi; Bce - Bacillus cereus; Bam-Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Bsu-Bacillus subtilis; Bli-Bacillus licheniformis; Bhc-Bhargavaea cecembensis; Ssi-Solibacillus silvestris; Sor-Streptococcus oralis; Sga-Streptococcus gallolyticus. * indicate conserved residues and † indicates residues forming a potential hydrophobic patch that were mutated in this work. (b) Model of S. aureus EsaB with positions of conserved residues targeted for mutagenesis highlighted. The N- and C-termini are also indicated. (c) and (d) RN6390 harbouring empty pRAB11, and the isogenic esaB deletion strain harbouring pRAB11, or pRAB11 encoding native, the indicated variants of EsaB were cultured aerobically in TSB medium until an OD600 of 2 was reached. Samples were fractionated to give cells and supernatant (sn), and supernatant proteins were precipitated using TCA. For each gel, 10 µl of OD6001 adjusted cells and 15 µl of culture supernatant were loaded. Blots were probed with anti-EsxA, and anti-TrxA (cytoplasmic control) antisera. (e) The ΔesaB strain harbouring pRAB11 encoding EsaB-YFP (WT-YFP) or the T8A or T8R amino acid-substituted variants were cultured in TSB medium until mid-log phase and separated into cellular and supernatant fractions (sn). For each sample, 10 µl of OD6001 adjusted cells and 15 µl of culture supernatant were loaded and blots were probed with anti-EsxA, anti-TrxA or anti-GFP antisera. The cell samples and supernatant samples have been blotted on the same gels but intervening lanes have been spliced out.