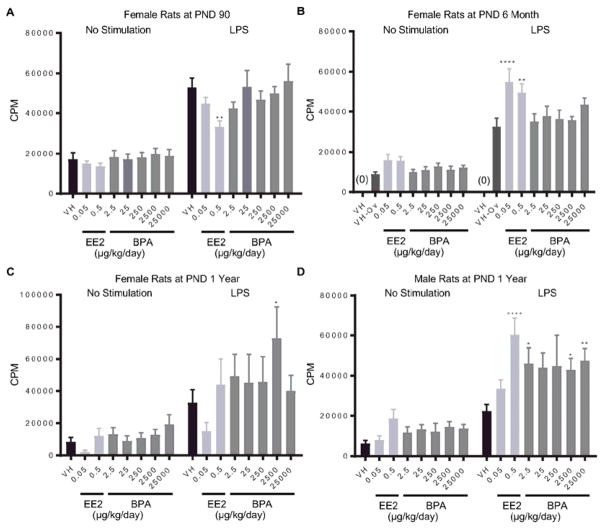
Figure 1. Quantification of LPS-induced spleen cell proliferation by treatment group and sex.
Female (A, B, C) and male (D) rats were administrated vehicle (VH, 0.3% aqueous carboxymethylcellulose), BPA or estrogen ethinyl estradiol (EE2) at the indicated dose level by oral gavage daily and sacrificed at postnatal day (PND) 90 (A), 6 month (B), and 1 year (C, D). Splenocytes were isolated and treated with LPS for 48 h after a 24 h pulse with [3H]-thymidine. Cells were harvested and quantified for [3H]-thymidine incorporation using a Tri-Carb 2100 TR scintillation counter, which is represented as counts per minute (CPM),. Results are presented as mean ± SE. n = 6–10 rats/treatment group/sex. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 when compared to respective vehicle control (VH-Ov for female rats at PND 6 month) by a two way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posttest. For more details about VH-Ov, please see the Statistical Analysis section in the Materials and Methods.