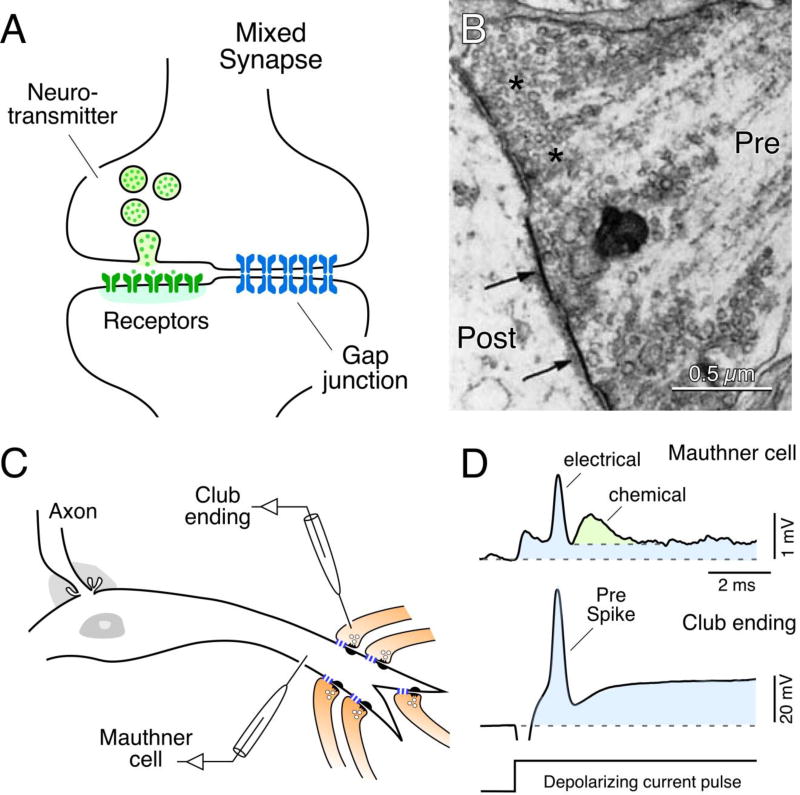
Fig. 1.
Mixed synapses in goldfish brain and their electrophysiological properties. (A) Diagram of a mixed synapse, at which a nerve terminal transmits both chemically via neurotransmitter and electrically via a gap junction. (B) Early thin-section TEM image of a portion of a Club ending synapse on a goldfish Mauthner cell, showing specializations for chemical transmission and nearby gap junctions (arrows) at contacts between presynaptic auditory afferents and postsynaptic Mauthner cell. Modified from [30], with permission. (C) Simultaneous in vivo pre- and postsynaptic recordings from a Club ending (recorded intracranially) and the lateral dendrite of the Mauthner cell. (D) Club endings exhibit mixed synaptic transmission. Presynaptic current injection (depolarizing current pulse) evokes a depolarization of the presynaptic terminal that is suprathreshold for spike generation (Pre spike). Both the coupling of the presynaptic spike and membrane depolarization were recorded in the postsynaptic lateral dendrite (blue overlay). A slower glutamate-mediated response (green) follows the electrical potential (blue area under the peak), or spikelet, evoked by the presynaptic spike. Traces represent the average of at least 10 individual responses. Panels C and D from [55].