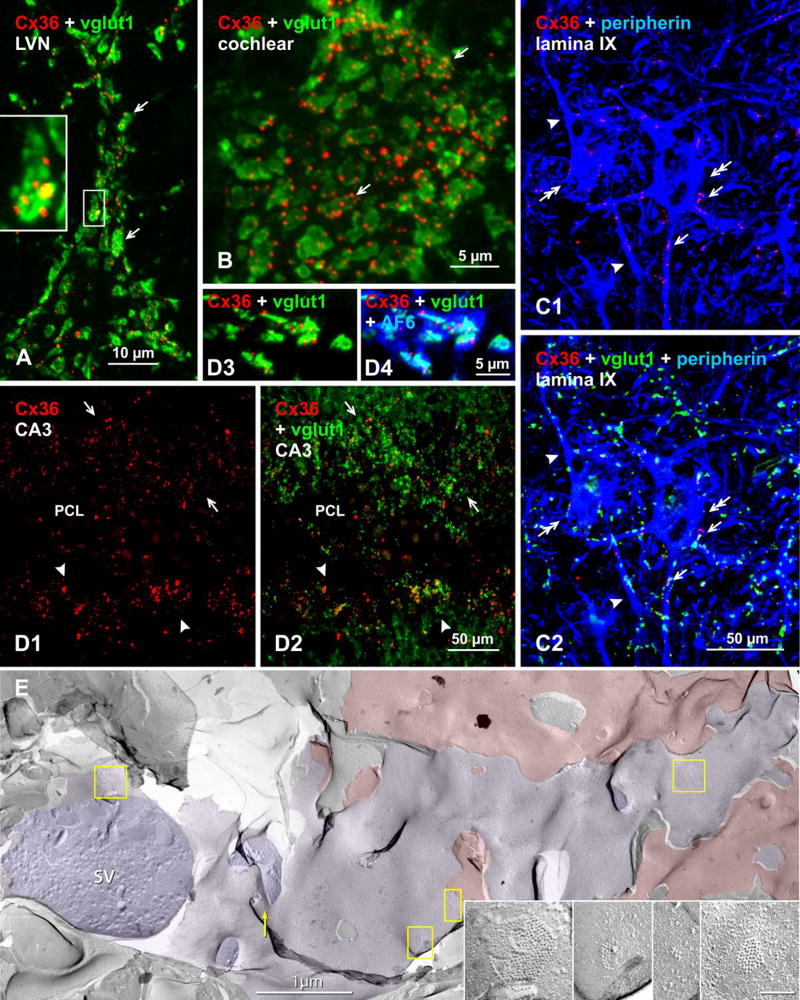
Fig. 3.
Immunofluorescence evidence for mixed synapses in various adult mouse and rat CNS regions, based on co-localization of Cx36 with the vglut1 marker of axon terminals. Color code for immunolabeled protein in overlay images is indicated in the upper left of each panel. (A) Lateral vestibular nucleus, where overlay of labeling for Cx36 and vglut1 shows a single neuronal cell body (not counterstained) contacted by large vglut1-positive axon terminals co-localized with labeling for Cx36 (arrows). The boxed area showing a single terminal is magnified in the inset. (B) Cochlear nucleus, where a similar overlay image shows vglut1-positive terminals decorated with Cx36-puncta (arrows) on a root neuron. (C) Spinal cord thoracic ventral horn lamina IX motor nucleus, where labeling for the motoneuron marker peripherin shows motoneurons (C1, double arrows), with Cx36-puncta decorating the somata (C1, arrows) and dendrites (C1, arrowheads) of those motoneurons, and in the same field labeled in addition for vglut1 showing Cx36-puncta co-localized with vgut1-positive axon terminals (C2, arrows). (D) Rat ventral hippocampal CA3 stratum lucidum, where Cx36-puncta straddling the pyramidal cell layer (PCL) dorsally (D1, arrows) and ventrally (D1, arrowheads) are largely localized to vglut1-positive mossy fiber terminals, as shown by labeling for Cx36/vglut1 in overlay (D2). Association of Cx36-puncta with vglut1, shown at higher magnification (D3), is also associated with labeling of the gap junction and adherens junction associated protein AF6 (aka, afadin) (D4). (E) Early freeze fracture image of mixed synapse between large axon terminal P-face (purple overlay) and overlying interneuron E-face (red overlay) in lamina VI of the lumbosacral adult rat spinal cord. (A small portion of this mixed synapse was published as a stereoscopic pair in Fig. 10 in [74]). Four gap junctions shared between the axon terminal and the interneuron are indicated (yellow boxes), and enlarged in insets.