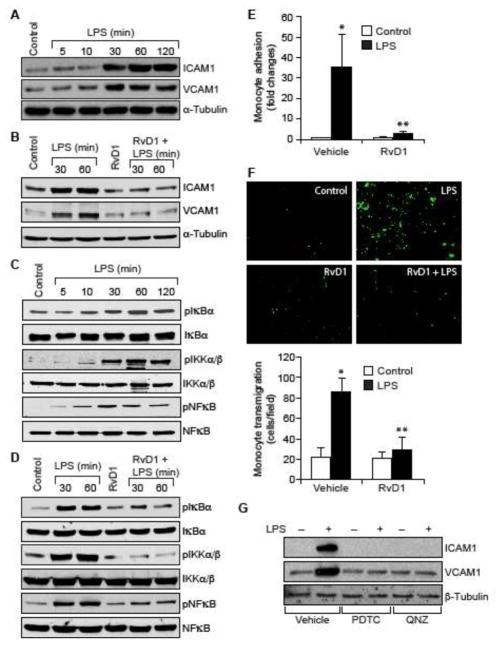
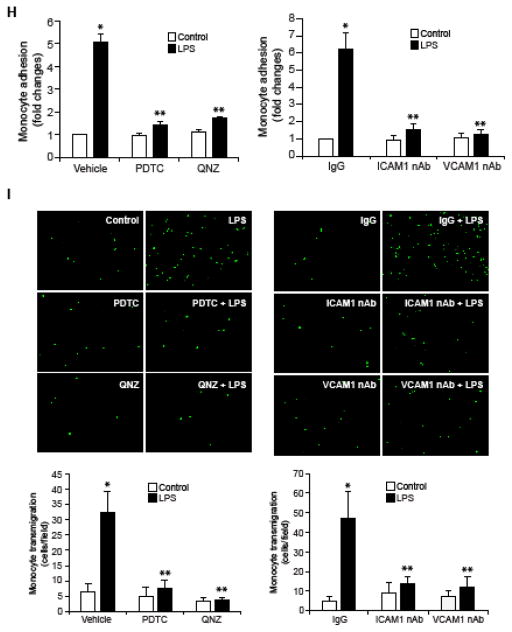
Figure 1. RvD1 attenuates LPS-induced EC-monocyte interactions via suppression of NFκB-mediated ICAM1 and VCAM1 expression.
A & C. Quiescent HUVECs were treated with and without LPS (500 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods and equal amount of protein from each condition was analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. B & D. Quiescent HUVECs were treated with and without LPS (500 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of RvD1 (200 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods and equal amounts of proteins from each condition were analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. E, F, H & I. Quiescent HUVEC monolayer was treated with and without LPS (500 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of RvD1 (200 ng/ml), PDTC (50 μM), QNZ (10 μM) or neutralizing ICAM1 or VCAM1 antibodies (2 μg/dish) for 2 hrs. After the treatments, the HUVEC monolayer was washed and BCECF-AM-labeled THP1 cells were seeded onto the monolayer and incubated for 1 hr for adhesion (E & H) and overnight for transmigration (F & I) assays. G. Quiescent HUVECs were treated with and without LPS (500 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of PDTC (50 μM) or QNZ (10 μM) for 1 hr and equal amount of protein from each condition was analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. The bar graphs represent quantitative analysis of three experiments. The values are expressed as Means ± SD. *, p < 0.05 vs control; **, p < 0.05 vs LPS.