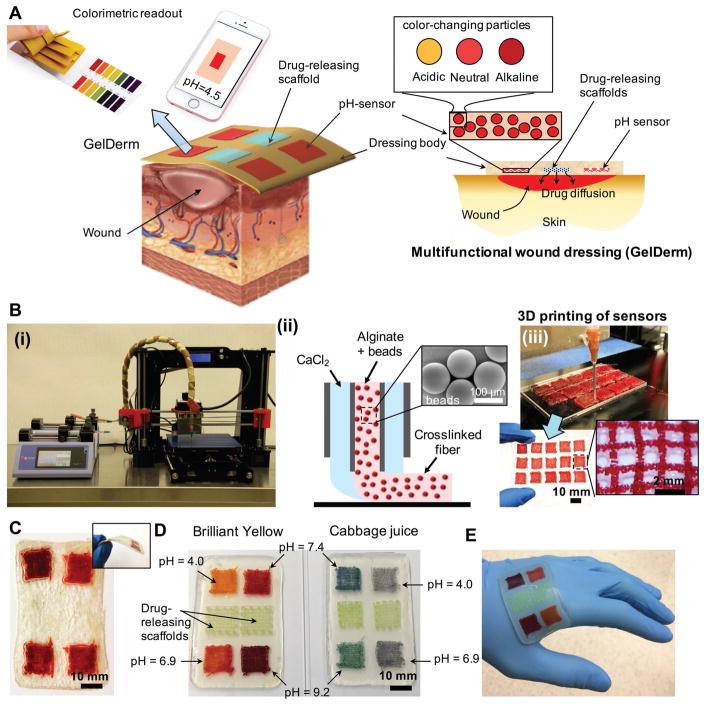
Figure 1.
An advanced multifunctional dressing (GelDerm) for monitoring and management of wounds. A) Schematic representation of GelDerm treatment of epidermal wounds, with pH-sensitive and drug-eluting components. B-i) Porous sensors were fabricated using a 3D bioprinter equipped with a co-axial flow microfluidic nozzle (i). B-ii) Schematic of fiber deposition using the co-axial flow system. B-iii) 3D printer can be programmed to produce arrays of porous sensors for fabrication of large-scale dressings. C) Dressings can be lyophilized and sterilized for storage and transportation. D) Synthetic Brilliant Yellow and naturally derived cabbage juice were used as model pH indicators for the fabrication of the sensors. Sensor arrays enable detecting spatial variations of pH on the wound site. Drug-eluting scaffolds release high doses of antibiotics at the wound site to eradicate the bacteria that may remain on the wound site each time the dressing is replaced. E) GelDerm can maintain a conformal contact with irregular surfaces.