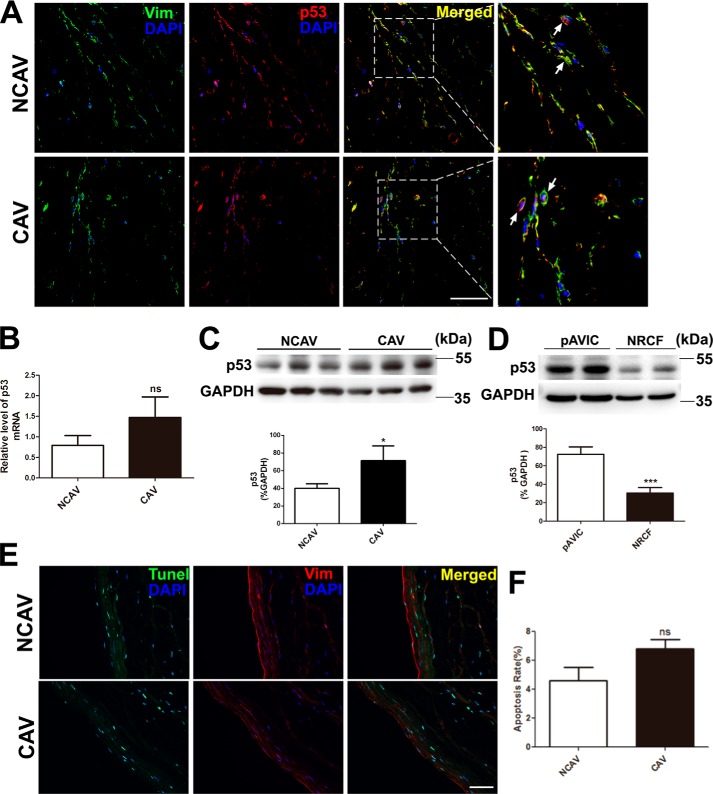
Figure 1.
p53 expression and the TUNEL assay in human aortic valves and pAVICs. Human calcific and non-calcific aortic valve tissues were harvested for immunostaining and qPCR. A, representative images of immunofluorescent staining of human aortic valves with the indicated antibodies. B, p53 expression levels in calcific and non-calcific human aortic valves were assessed by qPCR (n = 6 for each group). C, protein levels of p53 in calcific and non-calcific human aortic valves were assessed by Western blotting (n = 6 for each group). D, p53 protein levels in porcine AVICs and in rat cardiofibroblast cells were assessed by Western blotting. Relative protein levels were normalized to GAPDH. E, representative images of co-immunofluorescent staining of human aortic valves with the indicated antibodies and TUNEL. F, statistical analysis of apoptotic cells from stained valve sections (n = 6 for each group). Scale bar, 50 μm. Arrows indicate AVICs. Vim, vimentine; NCAV, non-calcific aortic valve; CAV, calcific rheumatic aortic valve; NRCF, cardiofibroblasts from newborn rats. The data are shown as the means ± S.E. of triplicates and are representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.