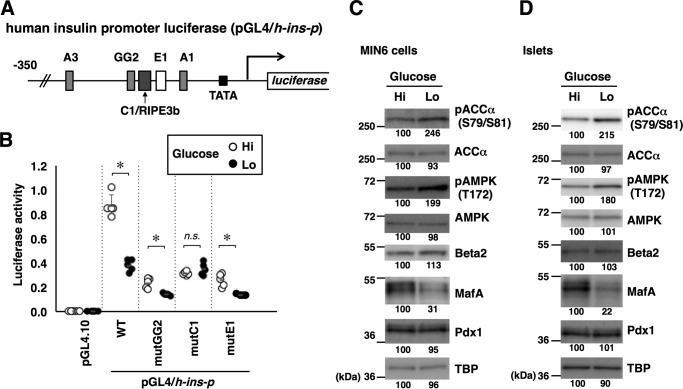
Figure 1.
Glucose regulates the insulin promoter, MafA abundance, and AMPK activity. A, schematic of the human insulin promoter reporter constructs. Locations of the binding sites for Pdx1 (A1, A3, and GG2), MafA (C1/RIPE3b), and Beta2/NeuroD1 (E1) are also indicated. B, the firefly luciferase reporter constructs (0.5 μg) indicated in A and a Renilla luciferase expression plasmid, pEF-Rluc (0.5 μg), were transfected into MIN6 cells, and the cells were incubated in medium containing high (Hi, 20 mm) or low (Lo, 2 mm) glucose for 16 h. Data are expressed relative to the activity in cells that received pGL4/h-ins-p (WT) under high-glucose concentration. Data are mean ± S.E. of five independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; n.s., not significant (Student's t test). C and D, MIN6 cells (C) or isolated mouse islets (D) were incubated in high-glucose (Hi, 20 mm) or low-glucose (Lo, 2 mm) medium for 16 h, and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. TBP was analyzed as a loading control. The data in C and D are representative of two independent biological experiments. The intensity of the bands was quantified using ImageJ software, and the relative amounts (averages of two independent experiments) are indicated below the bands.