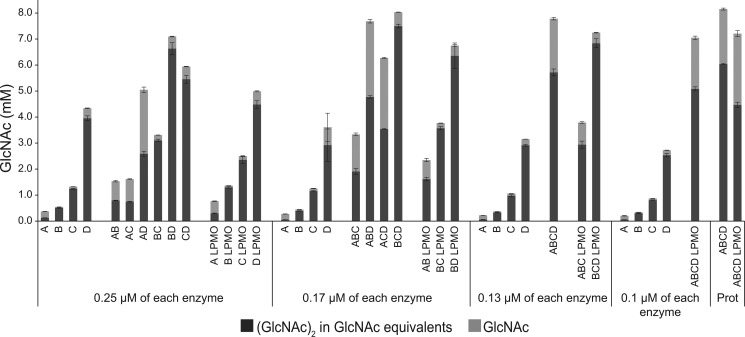
Figure 6.
Synergy experiments. The catalytic domains of all chitinases and the CjLPMO10A were mixed in different ways to investigate possible synergistic effects in reactions with α-chitin (15 g/liter). The maximum total enzyme load was 0.5 μm with equal amounts of each enzyme, as indicated in the figure. In the reactions where the ratio was determined by protein quantification data from a previous proteomics study (Prot) (22), the total enzyme loading was also 0.5 μm. In the proteomics reaction without CjLPMO10A, the ratio was 21% CjChi18A, 4% CjChi18B, 22% CjChi18C, and 52% CjChi18D. In the proteomics reaction with CjLPMO10A, the ratio was 14% CjChi18A, 3% CjChi18B, 15% CjChi18C, 35% CjChi18D, and 33% CjLPMO10A. The CjLPMO10A was Cu2+-saturated before use. Reaction mixtures were incubated at 30 °C in 20 mm BisTris, pH 6.5, 0.1 mg/ml BSA, and samples were taken after 24 h. In reactions with CjLPMO10A, 0.5 mm ascorbate was added as an external electron donor. Production of GlcNAc and (GlcNAc)2 was quantified, and the amount of (GlcNAc)2 is given in GlcNAc equivalents. Three parallel reactions were done for each condition and standard deviations are shown as error bars. Reaction mixtures that contained the LPMO showed minor amounts of oxidized (GlcNAc)2, which were not quantified.