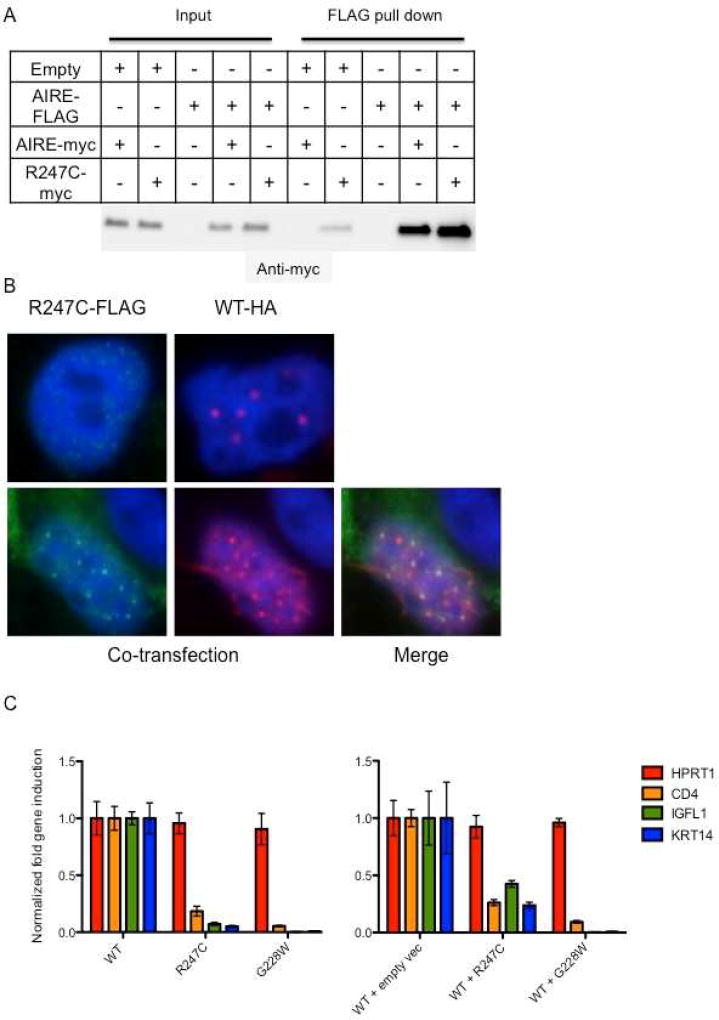
Figure 2. R247C impairs transcriptional regulation of WT AIRE.
Panel A shows that R247C forms complexes with WT AIRE. WT AIRE-FLAG was co-transfected with R247C-myc and complexes precipitated with anti-FLAG M2 beads. Eluted proteins were probed with anti-myc rabbit antibody. Panel B demonstrates the formation of nuclear punctae by R247C. WT AIRE-HA and R247C-FLAG were transfected into HEK293T cells and visualized using fluorescent secondary antibodies to either HA or FLAG. Multiple images were taken and staining patterns were compared for presence of cytoplasmic staining and nuclear punctae. Both WT AIRE and R247C demonstrated nuclear punctae with minimal cytoplasmic staining. When cotransfected, WT AIRE and R247C overlap, indicating likely complex formation. Panel C shows that HEK-293T cells transfected with either the patient mutation R247C or the known dominant negative mutant G228W produced less downstream gene transcripts than WT AIRE. Likewise, when WT AIRE and mutant AIRE were simultaneously transfected into HEK293T cells, downstream gene expression was decreased compared with cotransfection of empty vector and WT AIRE. qPCR was used to examine the expression of AIRE-regulated genes CD4, IGFL1, and KRT14 along with the AIRE-independent gene HPRT1. Expression levels were normalized against the endogenous control GAPDH. The results (mean ± SD) are shown as fold gene induction as compared to cells transfected with WT AIRE. The data is representative of two independent experiments. Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4); IGF-life family member 1 (IGFL1); keratin 14 (KRT14); hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1); glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH).