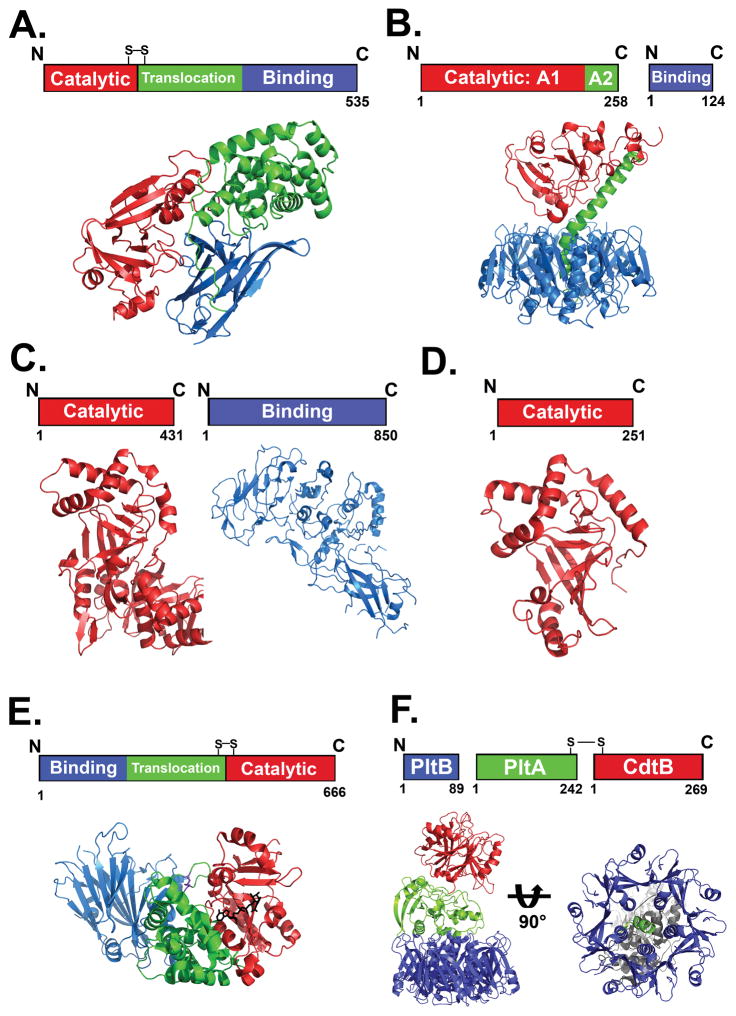
Figure 1. Structure-function organization of bARTT family members.
A. Diphtheria toxin (DT)-like toxins are single chain polypeptides possessing a catalytic A domain linked by a disulphide bond to a B domain that includes translocation and binding capacity. The figure shows the domain organization of DT (PDB:1MDT) B. Cholera toxin (CT)-like toxins are dual chain proteins, with catalytic A1 and A2 domains that insert into a pore in the pentameric binding (B) domain. The figure shows the domain organization of CT (PDB:1XTC) C. C2-like toxin catalytic A and receptor binding B domains are expressed separately. The figure shows the domain organization of C2 toxin (A domain; PDB:2J3Z) and B domain PDB:2J42). D. C3-like transferases consist solely of a catalytic A subunit. The figure shows the A subunit of C3bot-transferase (PDB:1G24) E. Domain organization and crystal structure of Cholix toxin. Cholix is organized similar to PE, with the binding domain at the N terminus and the disulfide linked translocation and catalytic domain at the C terminus. (PDB:3Q9O) F. Domain organization and crystal structure of Typhoid toxin (TT). (PDB:4K6L). TT has A2B5 organization, with two catalytic subunits (Left). CdtB shows structure-function homology to the Cytolethal distending toxins and is linked to PltA by a disulfide bond. Displaying structure-function homology to the pertussis toxin S1 and S2 subunits, respectively, PltA inserts into a PltB pentamer (Right).