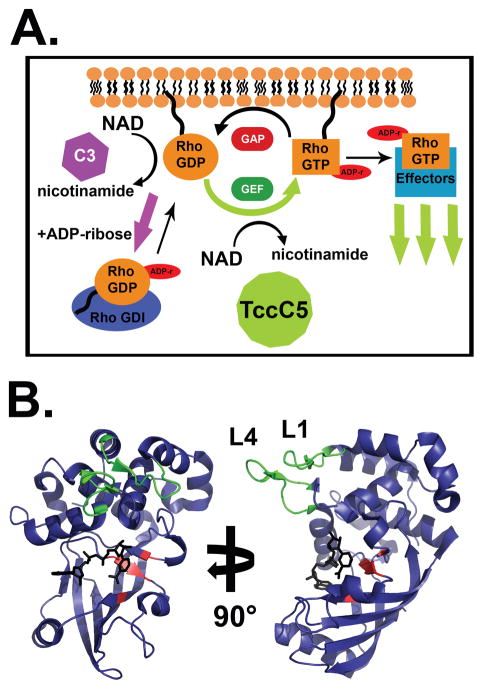
Figure 3. Modulation of Rho signalling by bARTTs.
A. Rho proteins cycle between active (GTP-bound) and inactive (GDP-bound) states at the plasma membrane, or can be bound by RhoGDI in the cytoplasm. GTP-bound Rho interacts with downstream proteins to effect signal transduction and actin stress fiber polymerization. C3 ADP-ribosylation of Rho results in an increased affinity for RhoGDI and sequestration of Rho in the cytoplasm, resulting in cytoskeletal collapse. Conversely, TccC5 ADP-ribosylation of Rho inhibits GTP hydrolysis and promotes constitutive Rho activation and stress fiber polymerization. B. Crystal structure of HopU1. HopU1 shows a conserved C3-like ADP-ribosyltransferase core structure (see Figure 1D) with unique regions responsible for substrate recognition. The “RSE” motif residues (red) and the novel substrate recognition loops L1 and L4 (green) are denoted (PDB:3U0J).