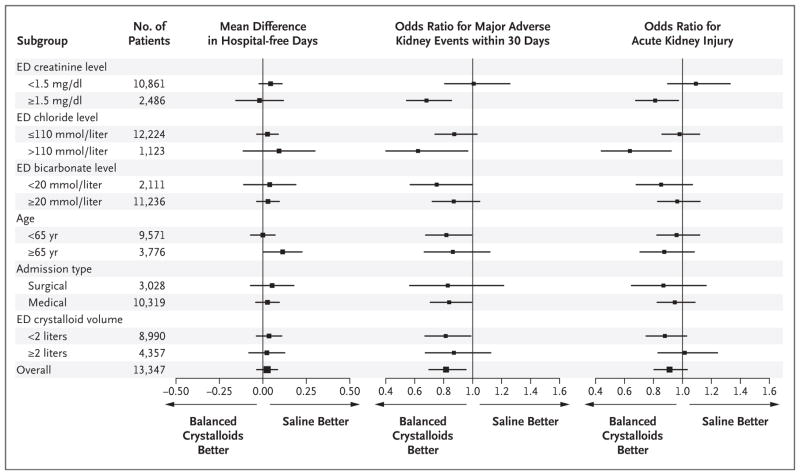
Figure 2. Heterogeneity of Treatment Effect.
Shown are forest plots for hospital-free days to day 28, major adverse kidney events within 30 days, and acute kidney injury of stage 2 or higher according to Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes creatinine criteria. The outcome of major adverse kidney events within 30 days was a composite of death from any cause, new renal-replacement therapy, or persistent renal dysfunction (defined as an elevation of the creatinine level to ≥200% of baseline) — all censored at hospital discharge or 30 days, whichever occurred first. Patients with end-stage renal disease who were receiving long-term renal-replacement therapy at the time of arrival in the emergency department (235 patients) were not eligible for the outcome of acute kidney injury; hence, the total sample size for the analysis of acute kidney injury was 13,112.