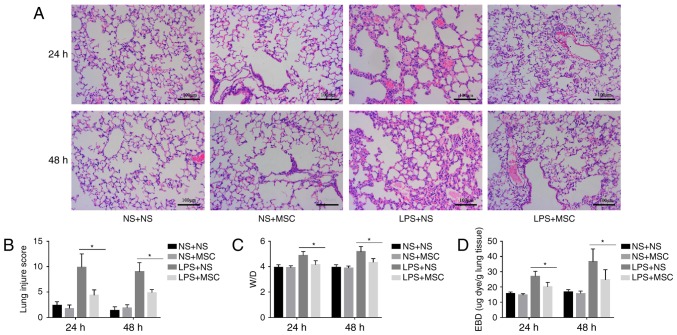
Figure 3.
Effects of hUC-MSCs on LPS-induced acute lung injury. (A) HE staining (magnification, ×200; scale bar=100 µm) of lung sections from LPS-challenged mice at 24 and 48 h showed marked interalveolar septal thickening, extensive inflammatory infiltration, diffuse interstitial and alveolar edema, and severe interstitial hemorrhage. The administration of hUC-MSCs in the LPS+MSC group improved the lung histopathology to differing degrees. (B) At 24 and 48 h, HE staining of the lung sections from hUC-MSC-treated mice in the LPS+MSC group had significantly less injury, compared with mice in the LPS+NS group. (C) Mice administered with hUC-MSCs in the LPS+MSC group showed a trend towards a lower lung W/D weight ratio at 24 and 48 h. (D) Dye accumulation in the lungs increased markedly at 24 and 48 h in the LPS+NS group, and was reduced by hUC-MSC treatment at 24 and 48 h. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=8 per group). *P<0.05. hUC-MSCs, human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NS, normal saline; W/D, wet/dry ratio; EBD, Evans blue dye.