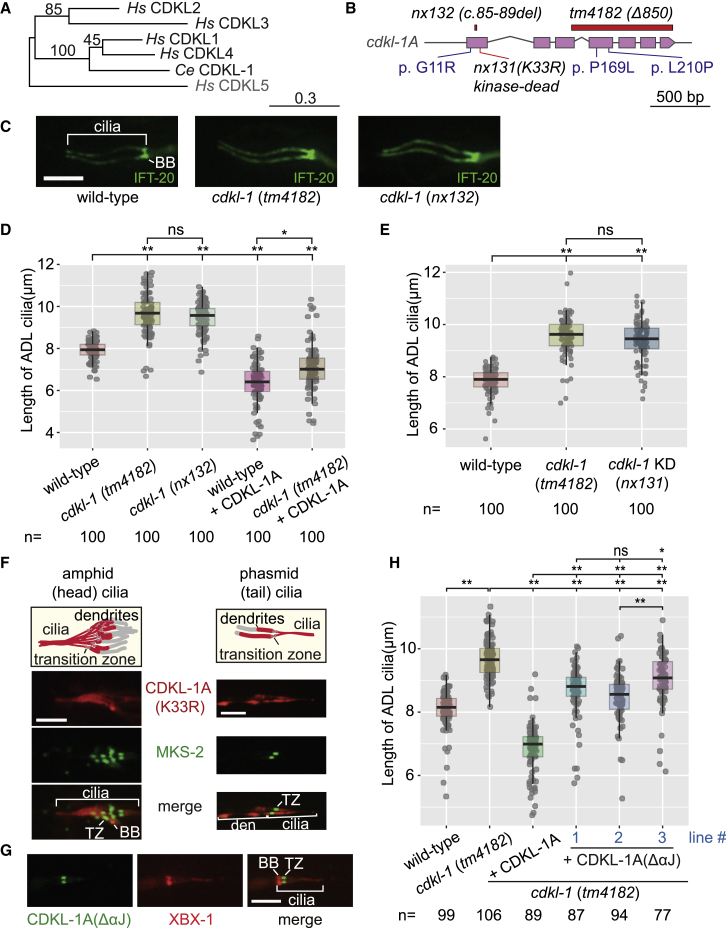
Figure 3.
C. elegans CDKL-1 Requires Its Kinase Activity and C-Terminal Region (Including αJ Helix) to Regulate Cilium Length
(A) Phylogenetic relationship between H. sapiens (Hs) and C. elegans (Ce) CDKL proteins.
(B) Gene structure of cdkl-1A, highlighting the deletion or missense mutants analyzed.
(C) Representative images of the GFP-tagged IFT-20 marker expressed specifically in ADL neurons (L4 larvae), used to measure the length of cilia in WT and cdkl-1 mutants (tm4182 and nx132). ADL doublet cilia are longer in mutants than WT. BB, basal body. Scale bar, 4 μm.
(D) ADL cilia lengths (L4 larvae) of WT and cdkl-1 mutants with/without expression of WT CDKL-1A construct. Each dot represents one cilium. Kruskal-Wallis test (Dunn Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison [Holm-Sidak method]) was used for significance in (D), (E), and (H). ∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
(E) ADL cilia length in WT, cdkl-1 null (tm4182), and cdkl-1 kinase-dead (KD) (nx131) mutant L4 larvae. Dot, one cilium. ∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
(F) The kinase-dead variant CDKL-1A(K33R)::tdTomato no longer concentrates at the TZ (marked by MKS-2::GFP); it mislocalizes to dendrites (den) and cilia in amphid and phasmid neurons. BB, basal body. Scale bar, 4 μm.
(G) CDKL-1A(ΔαJ)::mNeonGreen protein predominantly accumulates at the TZ in cilia. The BB and ciliary axoneme are marked by XBX-1::tdTomato. Scale bar, 4 μm.
(H) ADL cilia lengths (L4 larvae) measured in WT, cdkl-1 null (tm4182), and cdkl-1 null (tm4182) expressing CDKL-1A or CDKL-1A(ΔαJ). Dot, one cilium. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.