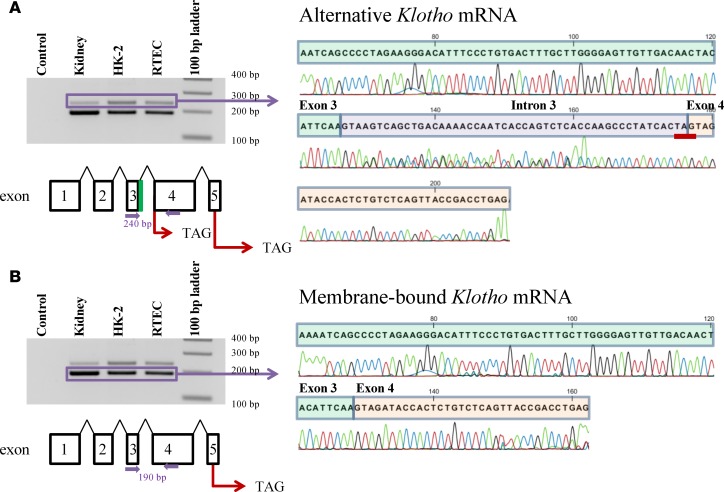
Figure 1. Identification of human Klotho mRNA transcripts by RT-PCR and DNA sequencing.
(A) The alternative Klotho mRNA transcript is detected in human kidney, primary renal tubular epithelial cells, and in the human HK-2 renal cell line. PCR using primers spanning exons 3 and 4 (indicated by closed purple arrows) yields 2 PCR products. DNA sequencing confirms that the 240 bp PCR product corresponds to the alternative Klotho mRNA, which contains a 50 bp insertion (purple) between exon 3 (green) and 4 (orange), yielding a premature TAG stop codon (underlined in red). The alternative Klotho exons are depicted schematically, including the intronic sequence between exons 3 and 4 (green). (Note: nucleotide 145 in this sequence has similarly low signals for G and C, but is a G according to published sequences.) (B) The membrane-bound Klotho mRNA transcript is detected in human kidney, in primary renal tubular epithelial cells, and in the human HK-2 renal cell line. PCR using primers spanning exons 3 and 4 (indicated by closed purple arrows) yields 2 PCR products. DNA sequencing confirms that the 190 bp PCR product corresponds to the membrane-bound Klotho mRNA, which does not contain the 50 bp insertion between exon 3 and 4. The membrane-bound Klotho exons are depicted schematically.